When deciding how to maintain assets, the choice between predictive and reactive maintenance can significantly impact costs, downtime, and asset lifespan. Here’s the key takeaway: predictive maintenance consistently outperforms reactive maintenance in cost savings, reliability, and long-term planning.
Key Points:
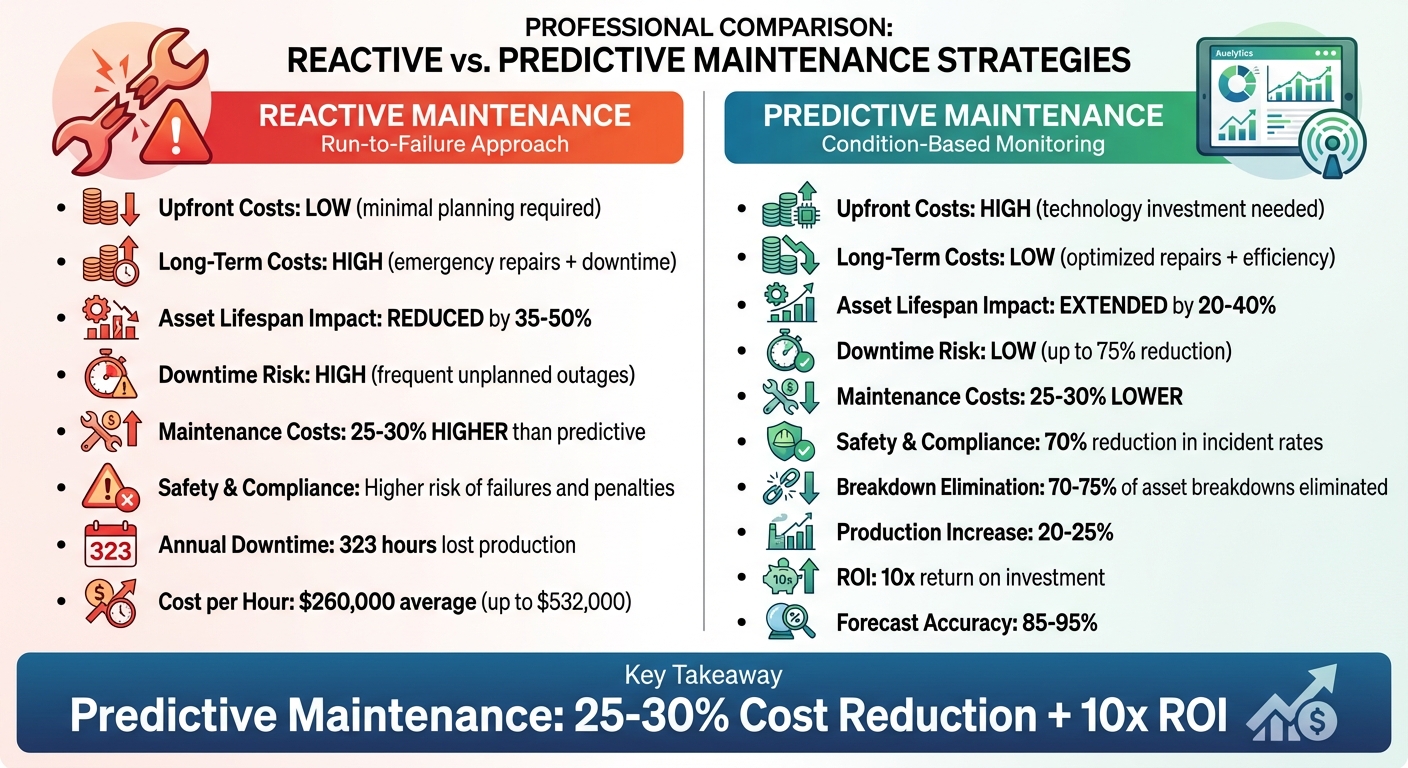
- Reactive Maintenance: Fixes issues after failure. It has lower upfront costs but leads to higher long-term expenses, increased downtime, and shorter asset lifespans.
- Predictive Maintenance: Uses sensors and analytics to prevent failures. While it requires higher initial investment, it reduces downtime by up to 75%, extends asset lifespans by 20–40%, and cuts maintenance costs by 25–30%.
Quick Comparison:
| Criteria | Reactive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Costs | Low – minimal planning required | High – investment in technology needed |
| Long-Term Costs | High – emergency repairs and downtime | Low – optimized repairs and efficiency |
| Asset Lifespan | Reduced by 35–50% | Extended by 20–40% |
| Downtime Risk | High – frequent unplanned outages | Low – up to 75% reduction |
| Safety & Compliance | Higher risk of failures and penalties | Lower risk with proactive monitoring |
Bottom Line: Predictive maintenance is a smarter choice for organizations aiming to reduce costs, avoid unexpected failures, and plan effectively for the future. If you’re managing critical assets, investing in predictive strategies offers measurable returns and long-term reliability.
Predictive vs Reactive Maintenance: Cost, Lifespan, and ROI Comparison
What Is Reactive Maintenance?
How Reactive Maintenance Works
Reactive maintenance is all about fixing things after they break. Often called "fix-on-failure", "run-to-failure", or "breakdown maintenance", this method requires little to no planning. Instead, it focuses on addressing problems as they arise to quickly restore functionality. For certain low-cost, non-critical items – like a light bulb in your home office or a flat tire – this approach makes sense. These failures don’t pose major safety risks, and replacing them is straightforward and inexpensive[10].
The Downsides of Reactive Maintenance
While reactive maintenance might seem simple, it comes with hefty costs. Emergency repairs can end up being three to four times more expensive than planned maintenance. Why? Think rush orders for parts, emergency service calls, and paying for overtime labor – all of which add up fast[11].
Then there’s unplanned downtime, which can wreak havoc on operations. In the manufacturing world alone, unexpected disruptions cost over $50 billion annually. Industrial plants can lose anywhere from $10,000 to $250,000 for every hour they’re offline[9]. As highlighted in Asset Performance Management: Blazing a Better Path to Operational Excellence:
The cost of unplanned downtime can be devastating, ranging from an estimated $10,000 to $250,000 per hour for industrial plants.[9]
The problems don’t stop there. Relying on reactive maintenance can reduce an asset’s lifespan by 30–40% and increase energy use by 15–20%, which drives up overall operational costs[11]. Safety risks also climb because neglected equipment is more likely to fail catastrophically. This not only endangers workers but can lead to expensive compensation claims and regulatory penalties.
On top of that, reactive maintenance often traps teams in a vicious cycle, sometimes called a "maintenance death spiral." Constantly dealing with emergencies leaves little room for planned tasks, creating a never-ending backlog. Shockingly, studies reveal that up to 80% of industrial facilities underestimate their downtime costs by 200–300%, leaving them unprepared for the financial hit[9].
What Is Predictive Maintenance?
How Predictive Maintenance Works
Predictive maintenance shifts the focus from reacting to equipment failures to proactively preventing them. Instead of waiting for something to break, it uses data and analytics to predict when maintenance is needed. This approach relies on sensors and connected technologies that monitor equipment performance in real time [1][13][4][7].
Here’s the process: Sensors track key performance indicators like vibration, temperature, oil quality, sound, and motor performance. These sensors send real-time data to EAM/CMMS systems, where AI and machine learning algorithms analyze the information to detect patterns or anomalies [13][4][8][5][7]. By identifying potential issues early, these systems help predict failures and schedule maintenance before problems escalate [13][8][5].
This method optimizes maintenance schedules based on the actual condition of equipment, rather than relying on fixed time intervals or usage milestones [1][5][7]. As a result, maintenance happens only when necessary, cutting down on unnecessary tasks and costly surprises.
For asset managers, tools like Oxand Simeo™ take predictive maintenance to the next level. By combining probabilistic modeling, advanced data analysis, and a proprietary database of over 10,000 aging models and 30,000 maintenance laws, the platform simulates how assets age, fail, and consume energy over time. This data translates into multi-year CAPEX and OPEX plans, helping managers make precise investment decisions while meeting budget, energy efficiency, and carbon reduction goals.
These tailored maintenance schedules not only improve efficiency but also deliver measurable operational and financial benefits.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance offers impressive results, reducing downtime by 35–50% and extending asset lifespans by 20–40% [13][12]. Studies show that companies can eliminate 70–75% of asset breakdowns, increase production by 20–25%, and cut maintenance costs by 25–30% [5]. Many organizations report a return on investment as high as 10 times [5].
Compared to traditional preventive maintenance, predictive strategies can yield 8–12% more savings [5]. They also provide greater control and visibility, allowing teams to address equipment issues more effectively while avoiding overtime, unnecessary servicing, and excessive inventory costs [7].
Consider these examples: A manufacturer using vibration analysis increased its Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) from 500 to 2,500 hours, saving $1.6 million annually by preventing unplanned bearing failures [7]. In another case, oil analysis applied to 50 hydraulic presses reduced the Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) by 60%, slashing downtime from 500 to 80 hours per year [7]. Similarly, temperature monitoring helped one organization improve its Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) from 88.9% to 97.3% by minimizing performance losses [7].
Predictive maintenance also aligns with sustainability efforts. By extending the lifespan of assets and optimizing energy consumption, it helps organizations lower their carbon footprint and adhere to regulatory standards. Tools like Oxand Simeo™ enable companies to integrate energy efficiency and CO₂ reduction targets into their maintenance plans, ensuring that operational decisions support broader environmental objectives.
Reactive vs. Predictive Maintenance: Side-by-Side Comparison
Comparing Costs, Lifespan, and Risk
At first glance, reactive maintenance might seem like the cheaper option because it requires minimal planning. However, the long-term expenses tell a different story. Downtime, emergency repairs, and collateral damage often make reactive maintenance far more expensive over time.
"Did you know reactive maintenance and repair costs are around 25%-30% higher than those of predictive maintenance?" – Jennifer A. Caldwell, Aquanomix [14]
This highlights why it’s important to look beyond upfront costs and consider total ownership expenses. According to the US Department of Energy, companies using preventive maintenance can save 12–18% compared to reactive maintenance [5][2]. Predictive maintenance takes it a step further, delivering an additional 8–12% in savings over preventive programs. In fact, predictive maintenance can reduce costs by 25–30% and offers a 10x return on investment (ROI) [5][2][14].
| Criteria | Reactive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Costs | Lower – minimal planning investments [2][15] | Higher – requires investment in sensors, software, and training [5][14] |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Higher – emergency repairs, extensive damage, and lost production [5][2] | Lower – reduced downtime, optimized repairs, and extended asset life [5][2] |
| Asset Lifespan | Reduced by 35–50% due to failure-prone operations [16] | Extended by approximately 40% through early issue detection [16] |
| Downtime Risk | Very high – unplanned and often extended downtime [2][4] | Low – up to a 75% reduction in unplanned downtime [16] |
| Safety & Compliance | Higher risk of sudden failures and compliance breaches [5] | 70% reduction in incident rates through proactive hazard identification [16] |
| Inventory Costs | Higher – requires maintaining large safety stocks [5][15] | Lower – parts inventory optimized based on predicted needs [5][15] |
The data paints a clear picture: reactive maintenance often leads to additional costs from collateral equipment damage, which occurs in 45% of major failures [16]. On the other hand, predictive systems can forecast equipment failures with 85–95% accuracy, giving teams 2–8 weeks to address potential issues [16].
Pros and Cons of Each Strategy
While predictive maintenance is widely viewed as the smarter approach for reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan, each strategy comes with its own set of trade-offs. Here’s a closer look:
| Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive Maintenance | • Lower initial costs due to minimal planning investments [2][15] • Requires fewer staff and minimal preparation [5] |
• Significantly higher long-term costs [14] • Frequent equipment replacement and lost productivity [5][14] • Poor predictability complicating budget planning [2][15] • Higher overtime costs for emergency repairs [5][14] |
| Predictive Maintenance | • Reduced maintenance costs and lower total ownership expenses over time [5][14] • Extends equipment lifespan for long-term ROI [5][2][14] • Optimizes energy operation and minimizes spare parts inventory [5][15] • Significantly lower downtime [16] |
• High initial capital investment for diagnostic equipment and training [5][2][14][15] • Complex system implementation requirements [1] |
For those managing infrastructure or real estate, the choice between reactive and predictive maintenance isn’t always straightforward. A blended approach, guided by an Asset Criticality Analysis (ACA), can help prioritize equipment based on factors like safety, production impact, repair costs, quality, and redundancy [17]. Tools such as Oxand Simeo™ can assist in this process by using probabilistic modeling and a database of over 10,000 aging models to simulate the effects of different maintenance strategies on performance and costs.
sbb-itb-5be7949
Why Predictive Maintenance Is Better for Long-Term Planning
When Predictive Maintenance Delivers the Most Value
Predictive maintenance plays a crucial role in managing complex asset portfolios, especially where unexpected failures can lead to major financial and operational setbacks. On average, unplanned equipment failures cost businesses a staggering $260,000 per hour, with some industrial operations suffering losses as high as $532,000 per hour when critical production lines come to a halt [19]. Manufacturing facilities, in particular, face 323 hours of lost production annually due to unplanned outages, translating to an economic impact of $172 million per plant [19].
This approach becomes even more indispensable when dealing with assets that have strict compliance and safety requirements. For example, an insurer once denied a $280,000 claim for a wine storage system that failed to maintain mandated temperature settings, resulting in a $150,000 loss in the wine collection and voided insurance coverage. This incident highlights how predictive monitoring can protect both assets and compliance standards [20].
The importance of predictive maintenance is widely acknowledged in the industry.
"Predictive maintenance is more than a maintenance technique – it’s an essential strategy for asset management and maximizing the life cycle of your equipment." – AssetWatch [18]
For infrastructure and real estate portfolios prioritizing sustainability, predictive maintenance offers measurable advantages. It can reduce energy consumption by 15-20% and increase equipment lifespan by 20-40% [6][19]. Additionally, proactive compliance monitoring often leads to insurance premium reductions of 15-30% [20]. Among organizations that adopt predictive maintenance, 95% report positive returns, with 27% recovering their investment within just 12 months [19].
These benefits demonstrate the importance of using a data-driven platform like Oxand Simeo™ to enable predictive maintenance strategies.
How Oxand Simeo™ Supports Predictive Maintenance
Oxand Simeo™ utilizes model-driven intelligence to simulate asset deterioration, even in cases where IoT sensor coverage is incomplete or unavailable. With a database of over 10,000 proprietary aging models and 30,000+ maintenance laws developed over more than two decades, the platform predicts how assets will deteriorate, fail, and consume energy throughout their lifecycle. This enables organizations to adopt predictive maintenance strategies without relying solely on sensor data.
The platform also supports risk-based prioritization by integrating data on asset condition, criticality, and costs into long-term CAPEX and OPEX plans. These plans, which can span anywhere from 5 to 30 years, allow teams to simulate various scenarios and compare maintenance strategies based on budget constraints, service level goals, and sustainability targets. For example, infrastructure clients using Oxand Simeo™ have successfully reduced targeted maintenance expenses by 10-25%, while also lowering CO₂ emissions and energy consumption on a large scale.
For organizations navigating ISO 55001 compliance or European energy regulations, Oxand Simeo™ delivers audit-ready investment plans. Its multi-criteria approach evaluates risk exposure, lifecycle costs, service levels, compliance requirements, and carbon impact. This transforms maintenance from a reactive cost center into a strategic tool for long-term asset management.
Transition from reactive to predictive maintenance with asset health monitoring
Conclusion
When planning asset investments, predictive maintenance consistently outshines reactive maintenance across almost every measure. The numbers speak for themselves: companies adopting predictive strategies have cut asset breakdowns by 70–75%, increased production by 20–25%, and slashed maintenance costs by 25–30%, all while achieving an average ROI of 10 times their investment [5]. On the flip side, reactive maintenance depends on unpredictable emergency repairs, which can cost three to four times more than scheduled maintenance [6]. The choice is clear.
This shift from “fix it when it fails” to “predict and prevent” isn’t just about avoiding expensive surprises. It’s about taking strategic control of your assets. Predictive maintenance changes the game by turning maintenance into a forward-thinking investment strategy. This approach makes budgets more manageable and predictable, especially for organizations handling critical infrastructure or large real estate portfolios, where predictability is crucial.
Most organizations adopt predictive maintenance for high-cost, critical systems while using preventive or reactive strategies for less critical assets [8]. This tailored approach aligns with a broader, data-driven maintenance strategy. The key is understanding which assets need real-time monitoring and which can rely on routine checks.
If you’re ready to rethink your current maintenance strategy, start by identifying your most critical assets and pinpoint where unplanned downtime hurts the most. Tools like Oxand Simeo™ can make this transition smoother. With over 10,000 proprietary aging models, the platform uses data-driven insights to simulate asset aging and refine long-term CAPEX and OPEX plans. Its risk-based prioritization system helps determine what to invest in, when to act, and how much to allocate – all while ensuring compliance and advancing sustainability goals. This approach not only delivers immediate performance improvements but also strengthens long-term investment returns.
Though shifting to predictive maintenance requires organizational commitment [3], the benefits – lower costs, longer asset lifespans, reduced downtime, and better financial planning – make it a winning strategy for any organization looking to maximize its asset investments.
FAQs
What advantages does predictive maintenance offer compared to reactive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance stands out as a smarter approach compared to reactive maintenance, especially when it comes to managing assets effectively. By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, it can pinpoint potential problems before they escalate into expensive breakdowns. This proactive method helps cut down on unplanned downtime, reduce repair expenses, and even prolong the lifespan of equipment.
Another advantage is how it streamlines resource allocation. Instead of spreading efforts thin or addressing issues after the fact, predictive maintenance targets areas that genuinely need attention, avoiding unnecessary repairs. It also plays a crucial role in improving safety, staying compliant with regulations, and enabling more strategic long-term planning for asset investments. These factors make predictive maintenance a practical and cost-efficient choice for asset management across the United States.
How does predictive maintenance help extend asset life and cut costs?
Predictive maintenance is a game-changer when it comes to keeping equipment running smoothly. By spotting potential issues early, it allows for timely repairs, preventing minor problems from turning into major damage. This approach helps equipment last longer by reducing wear and tear and keeping it in top condition.
Another big win? Cost savings. Predictive maintenance cuts down on unexpected breakdowns, eliminates unnecessary part replacements, and fine-tunes maintenance schedules based on real-time performance data. By focusing on the actual condition of assets, it ensures resources are used wisely and keeps overall maintenance expenses in check.
What are the upfront costs involved in adopting predictive maintenance?
Implementing predictive maintenance comes with upfront costs in a few critical areas. These often include sensors and hardware for data collection, IoT infrastructure, advanced analytics tools, and training for your team. The total expense will vary based on the size and complexity of your equipment and operations.
Though the initial investment might seem steep, the long-term benefits can far outweigh the costs. Predictive maintenance helps extend the life of your assets, cuts down on unexpected downtime, and reduces overall maintenance costs. It’s a forward-thinking approach that promotes smarter asset management and more efficient decision-making.
