ISO 55001:2024 is the global standard for asset management, focusing on balancing performance, risk, and cost throughout an asset’s lifecycle. It introduces a structured way to manage assets proactively, using data-driven strategies rather than reactive maintenance. Released in July 2024, this update emphasizes risk benchmarks – quantifiable metrics that guide smarter decision-making for prioritizing asset risks.
Key Takeaways:
- Risk Benchmarks: Metrics to evaluate and prioritize asset risks systematically, moving away from guesswork.
- Core Principles: Value realization, alignment with goals, leadership, proactive risk management, and a lifecycle approach.
- Benefits: Improved reliability, risk reduction, regulatory compliance, and cost control.
- Steps to Build Risk Benchmarks:
- Create a detailed asset register.
- Assess failure likelihood using historical data.
- Evaluate failure impact (safety, costs, delays).
- Use a risk matrix to rank assets by priority.
- Application: Integrate benchmarks into Strategic Asset Management Plans (SAMP) for actionable and transparent investment decisions.
Tools like Oxand Simeo streamline this process by consolidating asset data, enabling predictive maintenance, and supporting ISO 55001 compliance through audit-ready reporting and continuous improvement features.
ISO55001:2024 (Why, What and How) – Martin Kerr
ISO 55001 Principles for Risk and Asset Management
ISO 55001:2024 is built around five key principles that guide organizations in managing their assets effectively. These principles ensure that day-to-day operations are directly linked to long-term objectives. The first principle, value realization, emphasizes that every asset must deliver measurable benefits aligned with the goals of the organization and its stakeholders. Similarly, alignment ensures that decisions – whether it’s replacing a single component or upgrading an entire facility – are always in sync with the broader organizational strategy [6].
Leadership plays a crucial role by requiring executives and managers to integrate asset management into business planning. This means allocating the right resources and ensuring that every team member understands how their actions impact the performance of assets [6].
The risk management principle addresses uncertainty proactively. Whether it’s asset failures, unexpected expenses, or regulatory challenges, risks must be identified, assessed, and mitigated before they escalate. This approach shifts asset management from reactive problem-solving to a structured process that safeguards value while aligning with organizational and stakeholder priorities [6][7].
Lastly, the lifecycle approach focuses on managing assets from acquisition to disposal. This principle ensures that decisions made at any stage – whether during maintenance or replacement – consider the asset’s entire lifecycle. By doing so, organizations can make smarter investments and plan maintenance in a way that supports long-term goals [6]. Together, these principles create a balanced framework that optimizes performance, manages risks, and controls costs, all while delivering measurable value to the business [3][4].
Key Concepts and Objectives of ISO 55001
ISO 55001:2024 provides a structured approach for developing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an asset management system. Its primary goal is to maximize the value of assets by balancing performance, risk, and costs throughout their lifecycle [6][3][2].
This standard encourages organizations to make well-informed decisions by considering risks, costs, and lifecycle performance before taking action. By adopting this proactive mindset, businesses can move away from reactive maintenance and create a risk-aware culture [6][4].
Another critical aspect of ISO 55001 is its focus on aligning asset management practices with the organization’s overall objectives. This ensures that resources are directed toward assets that are essential for achieving success and meeting stakeholder expectations [6][3].
How ISO 55001 Clauses Guide Asset Management Practices
The principles of ISO 55001 come to life through specific clauses that outline operational requirements. These clauses help organizations translate strategic ideas into actionable steps.
- Clause 4: Defines the scope of the asset management system and the Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP). It also requires organizations to understand stakeholder expectations and address internal and external factors, including climate change impacts introduced in the 2024 update [1][9].
- Clause 4.5: Establishes criteria for decision-making that align with organizational goals, risks, and opportunities, along with specifying methods and tools to be used [9][10].
- Clause 5: Focuses on leadership by requiring approval of the asset management policy, scope, and SAMP. It ensures that decision-making aligns with organizational objectives [9][10].
- Clause 6: Requires formal planning for risks and opportunities. This includes documenting the SAMP to address risks, prevent undesired outcomes, and promote continuous improvement [8][9][10].
- Clause 7.6: Stresses the importance of managing data quality. It mandates processes for ensuring reliable data and information, which are critical for accurate risk assessments [9].
- Clause 10.3: Focuses on predictive maintenance. Previously referred to as "Preventive Action", this clause emphasizes proactive decision-making by identifying optimal times for maintenance, renewal, or disposal. This approach supports a risk-based strategy by addressing potential issues before they escalate [9][10].
ISO 55001 Terminology Explained
Understanding the key terms in ISO 55001 is essential for applying its principles effectively. An asset refers to anything that holds potential or actual value for an organization. This can include physical equipment, infrastructure, software, intellectual property, or even human resources, though the focus here is primarily on physical assets.
Asset management involves coordinated activities aimed at deriving value from assets. This process balances performance, costs, risks, and opportunities across an asset’s lifecycle, going beyond basic maintenance to include strategic planning, financial oversight, risk evaluation, and performance monitoring.
An asset management system (AMS) is the framework that connects strategy to execution. It includes policies, objectives, and processes that guide asset management efforts. The Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) serves as a key document that translates organizational objectives into specific asset management goals. Acting as a bridge between high-level strategy and operational decisions, the SAMP ensures alignment across all levels of the organization.
How to Build Risk Benchmarks Under ISO 55001
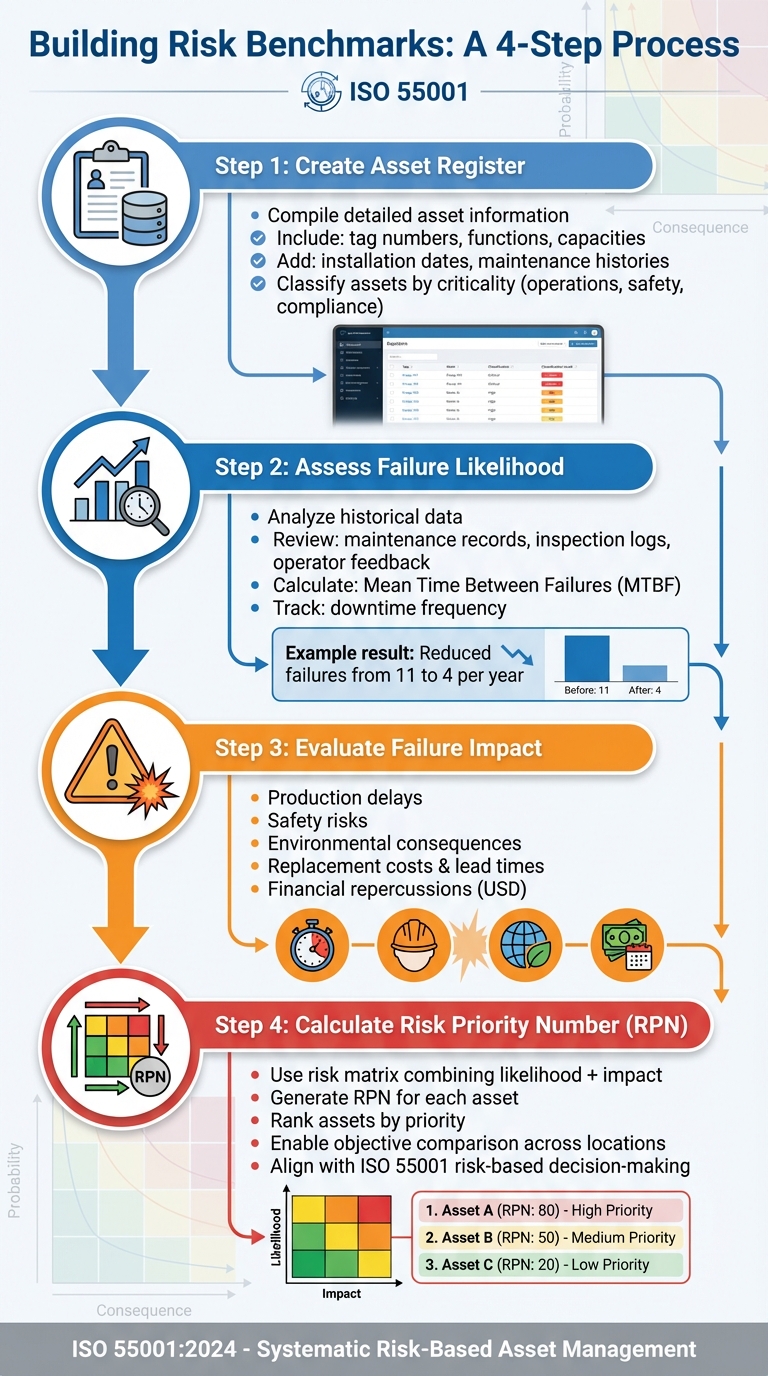
4-Step Process to Build ISO 55001 Risk Benchmarks for Asset Management
What Are Risk Benchmarks?
Risk benchmarks are tools that turn subjective asset risk evaluations into measurable KPIs, helping guide maintenance and investment decisions [4][5]. Instead of guessing or responding reactively to failures, these benchmarks allow you to pinpoint which assets pose the highest risk to operations, safety, or financial stability.
By setting clear criteria to evaluate assets – whether you’re overseeing a water treatment plant, a network of bridges, or a portfolio of commercial buildings – you can focus resources where they’ll make the biggest difference. For instance, if a critical pump scores high on a risk benchmark, it signals an urgent need for action to prevent costly downtime or safety issues. With this foundation, you can move forward with a structured approach to implement these benchmarks effectively.
Steps to Create Risk Benchmarks
Start by compiling a detailed asset register. This should include key details like tag numbers, functions, capacities, installation dates, and maintenance histories. Then, classify your assets based on their importance to operations, safety, and compliance [4]. Assets deemed highly critical – those whose failure could halt production or threaten safety – should be prioritized in your risk evaluation.
Next, assess the likelihood of failure by analyzing historical data such as maintenance records, inspection logs, and operator feedback. Use this information to calculate metrics like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and downtime frequency [4]. For example, one organization reduced failures in a high-risk pump from 11 to 4 in a single year by identifying and addressing lubricant contamination [4].
Evaluate the potential impact of asset failures, considering factors like production delays, safety risks, environmental consequences, and costs. Don’t overlook replacement lead times and financial repercussions [4]. Combine this likelihood and impact data in a risk matrix to calculate a Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each asset. This numerical ranking allows you to objectively compare risks across various assets and locations, aligning perfectly with ISO 55001’s emphasis on risk-based decision-making.
With these steps in place, ensure you’ve gathered the necessary data inputs to support precise risk evaluations.
Required Data Inputs for Risk Benchmarks
Building accurate risk benchmarks starts with a comprehensive asset register. Include details like tag numbers, functions, capacities, installation dates, operating conditions, and redundancy arrangements [4]. This information helps you see how each asset contributes to your overall operations.
Historical performance data is essential for meaningful risk assessments. Gather maintenance records, inspection logs, operator feedback, MTBF calculations, and downtime statistics [4]. Organizations that combine internal data (from systems like ERP and CMMS) with external benchmarks (such as industry standards and regulatory guidelines) are 25% more likely to meet their asset management targets [5].
Condition ratings also play a vital role. Assess assets based on factors like age, wear, and performance to guide maintenance priorities and capital planning [5]. Include financial data such as maintenance costs, lifecycle expenses, and investment needs in USD [4][5]. Real-time metrics – like condition monitoring outputs and performance data – allow for continuous tracking and informed decision-making. Predictive maintenance strategies that use these inputs can cut maintenance costs by up to 20% and reduce downtime by as much as 50% [5].
To keep your data organized and accessible, centralize it in an Asset Management Information System (AMIS). Regularly audit data quality and provide ongoing training on governance best practices to maintain the reliability of your risk benchmarks [5].
Converting Risk Benchmarks Into ISO 55001-Compliant Plans
Connecting Risk Benchmarks to Investment Plans
Once you’ve calculated your benchmark Risk Priority Numbers (RPNs), the next step is to turn those scores into actionable, budget-conscious plans. Start by ranking your assets based on their RPNs – those with higher scores demand immediate attention, whether through capital investment or maintenance efforts [4]. Under ISO 55001, a structured framework for risk-based decision-making is essential. This framework helps you evaluate how each asset impacts your business objectives and craft maintenance strategies grounded in clear, evidence-based assessments [4].
A well-organized investment plan tackles high-risk assets in the current fiscal year while deferring lower-priority items to future budgets. By documenting the reasoning behind these decisions, you enhance transparency and audit readiness. This step also ensures that stakeholders understand how asset priorities are determined.
Documenting Risk Benchmarks in Strategic Asset Management Plans (SAMP)
The Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) is the cornerstone for integrating risk benchmarks into your ISO 55001 compliance strategy. The 2024 update emphasizes the importance of predictive decision-making, robust data management, and effective risk control in SAMPs [11][12].
Your SAMP should clearly outline the methodology for risk assessments, the criteria for calculating RPNs, and the triggers for interventions across different asset categories. For instance, if your water treatment facility identifies several pumps as high-risk, each pump should be listed with its RPN, associated risks, planned interventions, timelines, and allocated budgets in USD. This level of detail not only meets ISO 55001’s standards for systematic asset management but also provides a comprehensive view of your approach to managing assets throughout their lifecycle [4][2].
Comparing Intervention Strategies
Choosing the right intervention strategy requires weighing the trade-offs between risk, cost, and performance. ISO 55001 emphasizes that risk assessments must guide these decisions, ensuring they align with your organization’s risk tolerance and financial constraints [4][13].
For assets with lower criticality, a run-to-failure strategy might be acceptable if replacement costs are minimal. On the other hand, preventive maintenance relies on scheduled interventions, while condition-based maintenance uses real-time data to trigger actions. Predictive maintenance takes it a step further by leveraging analytics to anticipate failures. When repair costs outweigh replacement value or when an asset reaches the end of its lifecycle, replacement or renewal becomes the logical choice. Be sure to document the rationale behind each strategy in your SAMP [4][13].
sbb-itb-5be7949
How Oxand Simeo Supports ISO 55001 Risk Benchmarks
Oxand Simeo simplifies the process of incorporating ISO 55001 risk benchmarks into strategic asset management, building on an established risk benchmarking framework.
Core Features of Oxand Simeo
The platform brings together asset data, condition assessments, and criticality information in one place to align with ISO 55001 risk benchmarks. This ensures that every investment decision is grounded in reliable, well-organized information – whether you’re managing infrastructure, buildings, or diverse real estate portfolios.
One of its standout capabilities is risk-based CAPEX and OPEX planning, which supports the development of long-term investment strategies spanning 5 to 30 years. With access to over 10,000 aging models and more than 30,000 maintenance laws, backed by two decades of expertise, Simeo uses a model-driven approach to predict asset deterioration. It achieves this by utilizing existing surveys, inspections, and operational data, eliminating the need for an extensive IoT sensor network.
Scenario Testing and Decision Optimization
Simeo’s scenario simulation feature allows users to test different budget allocations, service levels, and sustainability goals before committing to a plan. This tool makes it possible to compare various intervention strategies side-by-side, evaluating their impact on risk reduction, costs (in USD), and performance outcomes.
The platform also includes a multi-criteria prioritization engine, which evaluates factors like lifecycle costs, asset criticality, regulatory compliance, energy efficiency, and CO₂ emissions. This ensures that risk benchmarks are translated into well-rounded, strategic investment plans.
ISO 55001-Compliant Reporting
Oxand Simeo generates detailed, audit-ready reports that clearly outline your asset management strategy, making it easier to meet ISO 55001 compliance requirements.
Tracking and Improving Risk Benchmarks Over Time
ISO 55001 emphasizes the importance of ongoing improvement. Once you’ve set your risk benchmarks and aligned investment plans, the process doesn’t end there. Asset conditions change, regulations evolve, and operational priorities shift, making it essential to revisit and refine your strategies regularly.
Monitoring Key Performance Indicators
The first step to effective tracking is identifying the right KPIs. Organizations that use both internal and external data sources for KPI analysis are 25% more likely to meet their asset management objectives [5]. Some critical metrics to monitor include:
- Asset failure rates
- Safety incidents
- Budget variances
- Service level compliance
- Asset condition index
Regular reviews – whether quarterly or biannually – help ensure these benchmarks stay in sync with shifting business goals and market demands [5]. For example, changes in an asset’s criticality ranking can signal shifts in operational priorities or variations in performance. After these reviews, recalibrating your risk models becomes a necessary step to keep pace with changes in asset conditions.
Recalibrating Risk Models
Risk models are dynamic by nature. New inspection data, unexpected failures, and regulatory updates demand constant adjustments. ISO 55001 underscores the importance of learning from performance outcomes, audits, and stakeholder feedback to fine-tune risk management strategies over time [6][4]. This recalibration process involves:
- Comparing predicted asset deterioration against actual performance
- Updating aging models
- Adjusting risk scores when asset criticality changes
Revisiting investment plans with updated insights from the asset condition index ensures your assets continue to perform optimally [5].
Continuous Improvement with Oxand Simeo
Oxand Simeo takes continuous improvement to the next level by combining refined risk models with updated KPIs. The platform is designed to uphold data quality and track performance in line with ISO 55001 standards. With access to over 10,000 aging models and 30,000 maintenance laws, Simeo automatically integrates new inspection and operational data to improve predictions. Its dashboard simplifies the process by highlighting trends in asset data governance, making it easier to pinpoint when risk benchmarks need adjustment. Additionally, Simeo ensures all documentation is ready for audits, supporting ISO 55001’s focus on continuous improvement.
Conclusion: The Value of Risk Benchmarks in ISO 55001
Risk benchmarks play a key role in turning ISO 55001 from a compliance framework into a tool for strategic decision-making. By systematically assessing asset criticality, failure likelihood, and operational impact, organizations can direct maintenance budgets where they’re needed most – helping to prevent costly disruptions and safety risks [4]. This structured approach ensures a balance between asset performance, risk mitigation, and spending, delivering measurable results while reducing operational costs [2][3]. It also provides a solid foundation for well-justified investment and maintenance choices.
Organizations that combine internal and external data sources for performance analysis are 25% more likely to meet their asset management objectives [5]. This success stems from embedding risk-based decision-making into every investment decision.
ISO 55001 encourages organizations to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive, risk-aware management [4]. Risk benchmarks support this shift by offering the data needed to justify budgets, evaluate intervention strategies, and meet compliance requirements for auditors and stakeholders. The standard’s focus on continuous improvement ensures these benchmarks adapt as asset conditions and business needs evolve. Tools like Oxand Simeo enhance this process by providing dynamic solutions.
Oxand Simeo integrates aging models and maintenance frameworks to deliver audit-ready, continuously updated predictions. The platform automatically adjusts forecasts as new inspection data becomes available, keeps documentation up to date, and flags when benchmarks require recalibration – all in alignment with ISO 55001 standards.
When implemented effectively, risk benchmarks provide clarity, control, and confidence in asset management. They help organizations back up investment plans with solid, quantitative evidence, make smarter use of resources, and show how every dollar spent contributes to safer and more reliable operations. These benchmarks embody the core vision of ISO 55001: comprehensive and forward-thinking asset management.
FAQs
What are risk benchmarks, and how do they support better asset management decisions?
Risk benchmarks serve as measurable standards that help evaluate the performance, condition, and value of assets. These benchmarks allow organizations to pinpoint priorities, fine-tune maintenance schedules, and allocate resources more efficiently.
By adopting this method, companies can take a proactive stance on risk management. This not only ensures assets remain dependable but also helps control costs and keeps decisions aligned with the organization’s larger objectives. In essence, risk benchmarks bring clarity and structure to the decision-making process, enabling smarter, data-driven choices in asset management.
What are the key steps to establish risk benchmarks using ISO 55001?
To establish meaningful risk benchmarks under ISO 55001, start by thoroughly understanding your organization’s specific context and defining clear asset management goals. This foundation helps align risk management efforts with broader organizational objectives.
Next, create a structured risk management process and build a detailed asset register. This register is essential for assessing the criticality of each asset, identifying potential risks, and evaluating their likelihood and potential impact.
Once risks are identified, prioritize them using tools such as Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) to determine which issues require immediate attention. From there, design targeted strategies to mitigate these risks. Incorporating proactive maintenance practices, like condition-based or predictive maintenance, can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Make sure to document all actions taken and integrate this risk data into your asset management system. By doing so, you’ll not only enhance decision-making and ensure compliance but also support the long-term reliability and efficiency of your assets.
How does Oxand Simeo help organizations meet ISO 55001 standards and set effective risk benchmarks?
Oxand Simeo provides organizations with a robust, data-focused platform designed to align with ISO 55001 standards. This platform streamlines compliance by helping users assess how their assets support business goals, pinpoint potential risks, and set clear, measurable risk benchmarks.
Equipped with features like asset criticality analysis, condition assessments, and KPI tracking, Simeo empowers organizations to embrace risk-based decision-making and manage assets throughout their lifecycle. The result? Enhanced asset performance, better resource management, audit readiness, and smarter investment decisions grounded in reliable data.
Related Blog Posts
- Predictive Maintenance for Asset Management (Infrastructure and Real Estate) is critical – use the web site the web site:https://theiam.org
- Infrastructure Asset Management: A Risk-Based Approach for Multi-Year CAPEX Planning
- End-of-Concession Management for Highways: Strategic CAPEX Planning to Meet Grantor Requirements and Ensure Profitability
- Strategic CAPEX Planning for Highway Concessions: Balancing Grantor Compliance and Profitability at End-of-Term