Predictive maintenance isn’t just about avoiding breakdowns – it’s about reducing costs, extending asset lifespans, and improving operational efficiency. To calculate its ROI, you need to consider both direct savings (like fewer repairs and less downtime) and indirect benefits (like deferred capital expenses and reduced risk). Here’s a quick breakdown:
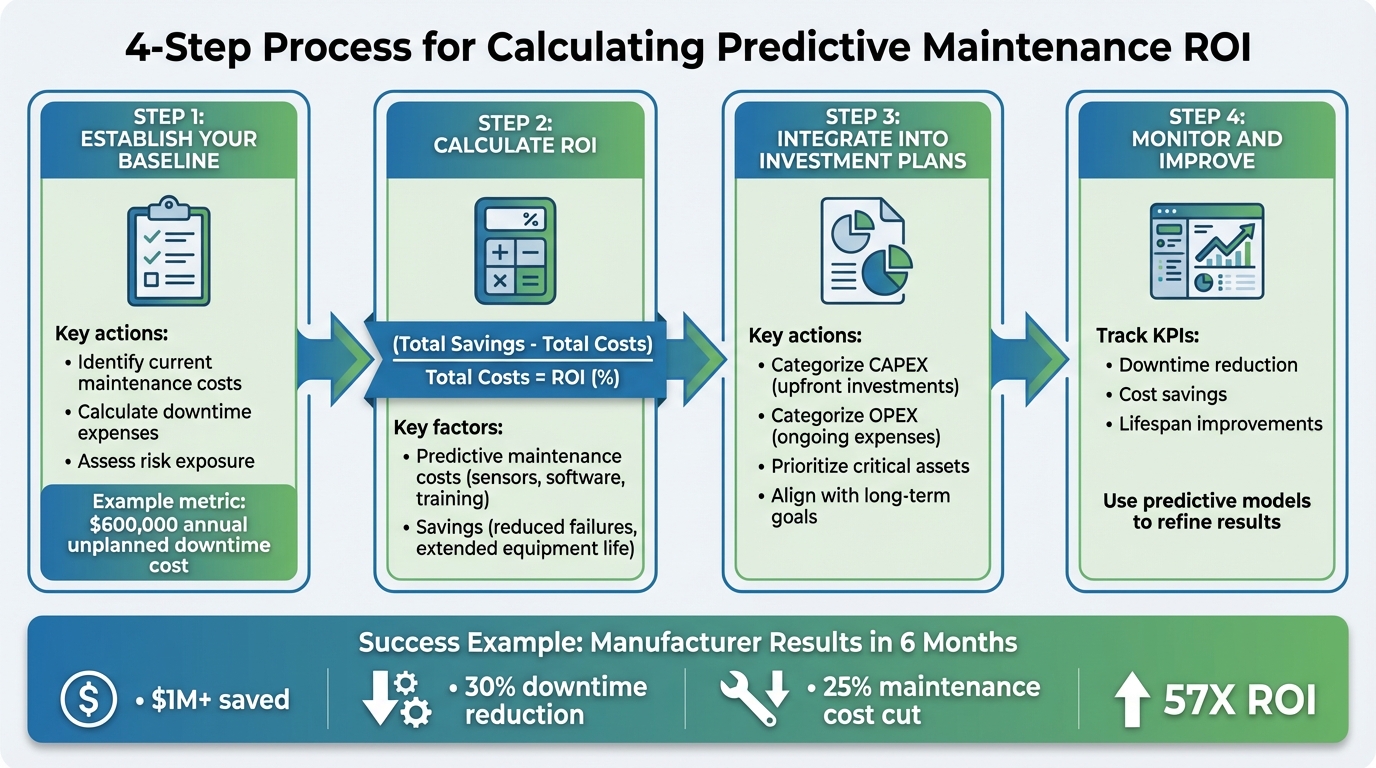
- Step 1: Establish Your Baseline
Identify current maintenance costs, downtime expenses, and risk exposure. For example, if unplanned downtime costs $600,000 annually, this becomes your starting point. - Step 2: Calculate ROI
Factor in predictive maintenance costs (e.g., sensors, software, training) and savings (e.g., reduced failures, extended equipment life). Use the formula:
(Total Savings – Total Costs) / Total Costs = ROI (%) - Step 3: Integrate ROI into Investment Plans
Categorize costs into CAPEX (upfront investments) and OPEX (ongoing expenses). Prioritize critical assets and align with long-term goals. - Step 4: Monitor and Improve
Track KPIs like downtime reduction, cost savings, and lifespan improvements. Use predictive models to refine results over time.
For example, a manufacturer saved over $1 million in six months by reducing downtime by 30% and cutting maintenance costs by 25%. Start with a pilot program, focus on critical assets, and expect measurable results within 12 months.
4-Step Process to Calculate Predictive Maintenance ROI
How Do You Calculate Predictive Maintenance ROI? – Air Traffic Insider
Step 1: Establish Your Financial and Risk Baseline
Before diving into predictive maintenance, it’s essential to understand where you currently stand. Start by assessing your maintenance costs, asset performance, and risk exposure. This will help you measure the potential return on investment (ROI) of predictive maintenance. From there, identify and prioritize the assets that are most critical to your operations.
Define Asset Scope and Criticality
Begin with an asset criticality analysis to pinpoint the equipment that poses the highest financial and operational risks.
"Criticality analysis – What are the biggest risks? Which critical equipment causes bottlenecks and has the highest cost when in downtime? Having those process-critical systems with enough preventable downtime mapped out will already provide a good base for a solid business case." – UReason [4]
Focus on assets that meet three essential criteria:
- Critical to operations: These are assets where downtime leads to significant financial losses or operational disruptions.
- Prone to failures: Equipment with a history of unexpected breakdowns.
- Measurable impact: Assets where you can track metrics like downtime, repair costs, and performance improvements.
For example, a manufacturing line’s primary conveyor system or a central HVAC unit in a commercial building often qualifies as high-criticality. Their failure directly impacts operations and revenue.
To streamline this process, maintain a centralized asset register. This should include standardized data for each asset, such as its age, condition, maintenance history, and operational importance. This register acts as your go-to resource for tracking performance and justifying predictive maintenance investments. Prioritize equipment with documented preventable downtime to build a strong business case [4].
Capture Baseline Financial Metrics
Once you’ve identified critical assets, gather financial data to establish your current costs. Use your CMMS and ERP systems to collect "business as usual" expenses [3][6].
Your baseline should cover:
- Reactive maintenance costs: Emergency repairs and unplanned fixes.
- Preventive maintenance costs: Regular inspections and routine servicing.
- Downtime costs: Lost production hours, missed deadlines, and penalties.
- Spare parts inventory expenses: Costs for maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) supplies and storage.
- Energy consumption: Expenses tied to inefficient equipment operation [3][6][4][5].
For instance, if your facility experiences 120 hours of unplanned downtime annually at $5,000 per hour, that’s $600,000 in downtime costs alone. These are the kinds of figures you’ll want to reduce.
Don’t forget indirect costs like production rejects, material waste, overtime labor, and regulatory penalties. Pull data from recent years to estimate realistic savings [6][4][7]. The more detailed your baseline, the easier it will be to showcase the ROI of predictive maintenance.
Convert Risk Exposure into Financial Terms
Risk exposure becomes more tangible when translated into financial liability. Start by identifying failure types for each critical asset, estimating their frequency, and calculating the associated costs – such as analysis, repair, downtime, and lost production [2].
Here’s an example: If a critical pump has a 15% annual chance of catastrophic failure, and such a failure would cost $250,000 in repairs plus $100,000 in lost production, the expected annual loss equals $52,500 (0.15 × $350,000). Using probabilistic aging and risk models can refine these estimates, especially for assets with complex failure modes or long lifecycles [2].
This quantified risk can be a powerful tool when presenting a business case to CFOs or executives. For instance, you can explain, "This asset alone exposes us to $52,500 in annual expected losses", and then show how predictive maintenance could reduce that risk.
Step 2: Calculate the True ROI of Predictive Maintenance
Once you’ve established your baseline, the next step is to calculate the ROI by breaking down costs and identifying savings. Start by listing your expenses and then quantify the benefits, both direct and indirect.
Identify Predictive Maintenance Costs
Begin by cataloging every expense associated with predictive maintenance. These typically fall into three key categories: technology investment, implementation and integration, and workforce development.
For technology investment, include the costs of IoT sensors, AI analytics platforms, a CMMS with predictive capabilities, computing infrastructure, and any retrofitting needed for older equipment [8][10][11].
Implementation costs include integrating these technologies with your existing ERP, SCADA, and operational systems. Don’t forget to account for consulting fees and system integration expenses.
"Implementing predictive maintenance requires investing in IoT sensors, AI analytics platforms and system integration. However, the long-term cost savings and efficiency gains outweigh the initial costs." – Dave Hopson, Founding Partner at Triumphus [8].
Finally, workforce costs encompass training your team to effectively use AI insights. You may also need to hire data scientists or domain experts. Given that 48% of maintenance professionals cite challenges in hiring, onboarding, and retaining skilled workers, allocating resources for comprehensive training programs is critical [10].
This detailed breakdown forms the "cost" side of your ROI equation.
Measure Cost Savings and Indirect Benefits
Next, quantify the savings. Start with direct savings, such as reduced emergency repairs, fewer unplanned shutdowns, lower spare parts usage, and decreased energy consumption.
For example, in 2025, a commercial office building using IBM Maximo for HVAC predictive maintenance detected a failing chiller unit early, saving an estimated $50,000 in downtime and emergency repair costs [8]. Similarly, ATS helped a building products manufacturer save over $40,000 by identifying a high-voltage transformer running hotter than normal, avoiding at least 12 hours of production downtime [9].
Indirect benefits also play a significant role. These may include extending the lifespan of assets, improving production quality with fewer rejects, reducing material waste, avoiding overtime labor for emergency fixes, and steering clear of regulatory penalties. Additionally, predictive maintenance reduces overall risk by minimizing exposure to unexpected failures.
Translate these savings into annualized dollar amounts. For instance, if you prevent three major equipment failures each year, each costing $100,000, you’re saving $300,000 annually. Similarly, if asset lifespans are extended by 20%, calculate the deferred replacement costs spread over those additional years.
Apply ROI and Payback Formulas
To finalize your ROI, use the standard formula: (Total Savings – Total Costs) / Total Costs = ROI (%) [5]. Alternatively, you can calculate it as (Increased Revenue + Decreased Cost) / Cost of PdM Solution [12].
For example, a $200,000 predictive maintenance program that saves $350,000 annually delivers a 75% ROI in the first year. The payback period – the time it takes for savings to equal costs – would be about 6.9 months.
You can also calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) by applying your standard discount rate (typically 3–7% for public organizations, higher for private ones) to account for long lifecycle assets.
Run sensitivity analyses to explore different scenarios. For instance, consider the impact of a 20% change in downtime costs, a 30% reduction in sensor prices, or a faster-than-expected decline in failure rates. These analyses help you gauge potential outcomes and strengthen your business case, especially when presenting to CFOs who are focused on understanding risk exposure along with potential gains.
sbb-itb-5be7949
Step 3: Integrate ROI into Your Risk-Based Investment Plan
Transform the ROI from your predictive maintenance efforts into a multi-year investment strategy that balances financial gains, risk mitigation, and long-term goals.
Map ROI into CAPEX and OPEX Profiles
The first step is to categorize your predictive maintenance costs into capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operational expenditures (OPEX). Think of CAPEX as the upfront investments – like sensors, analytics platforms, and system integration – while OPEX covers ongoing expenses, such as software subscriptions, support contracts, and the labor of your predictive maintenance team.
One major benefit of predictive maintenance is how it extends the lifespan of assets, deferring significant CAPEX. For example, if predictive maintenance extends the life of a $500,000 HVAC system by five years, that deferred expenditure should be factored into your long-term CAPEX planning. This not only frees up resources but also improves cash flow over time.
For a more complete financial picture, consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) instead of focusing solely on ROI. TCO accounts for all costs – initial and recurring – balanced against the asset’s annual benefits over its lifecycle. Take the example of a cement manufacturer that saved over $1 million in just six months without any CAPEX, achieving a 57× ROI [13]. These kinds of results become clear only when you map out the full cost-benefit profile over several years.
Once you’ve categorized and mapped these costs, focus on prioritizing investments by weighing financial returns alongside risk factors.
Prioritize Using Multiple Decision Criteria
While financial metrics like ROI are important, they don’t tell the whole story. You also need to evaluate investments based on risk, asset criticality, and sustainability goals. Assets critical to safety, compliance, or operations should take precedence, even if their ROI appears less impressive on paper. Failure of high-criticality assets can lead to safety incidents, regulatory fines, or major service disruptions – costs that simple financial metrics often overlook.
To make informed decisions, use a weighted scoring system. This allows you to assess investment scenarios under constraints like budget limits, operational requirements, and sustainability targets. Advanced platforms with thousands of aging models and maintenance laws can help you analyze lifecycle costs, the criticality of assets, and even CO₂ impact, all at once.
Run Scenario Planning and Sensitivity Analyses
Predictive maintenance ROI is not set in stone – it depends on variables like asset failure rates, detection accuracy, and how much longer assets can actually last [6]. That’s why scenario planning is a must.
Create different scenarios to focus on quick wins, protect critical assets, or achieve sustainability milestones. Test these scenarios against variables like a 20% rise in downtime costs, a 30% drop in sensor prices, or faster-than-expected reductions in failure rates. Using conservative estimates as your baseline can help you build trust with CFOs and boards. Overestimating savings or underestimating costs are common pitfalls to avoid [5].
Step 4: Set Up Governance and Continuous Improvement
Once ROI calculations are incorporated into investment plans, the next step is to ensure these benefits are sustained through proper governance and a focus on continuous improvement.
Establish Governance for Predictive Maintenance ROI
Start by defining clear roles within your team: asset owners evaluate the long-term impacts of investments, operators handle day-to-day maintenance tasks, finance teams monitor costs and savings, and sustainability managers focus on aligning efforts with energy and carbon reduction goals. A well-structured governance framework – built around the principles of People, Processes, Parts, and Performance – is key to maintaining equipment reliability and operational efficiency [14]. Aligning this framework with standards like ISO 55001 elevates your predictive maintenance program from being seen as just another expense to being recognized as a strategic asset [1].
Regular KPI monitoring is essential to this governance model. By reporting progress to stakeholders consistently, you can ensure the program stays aligned with broader business objectives and investment strategies.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Tracking the right KPIs provides a clear picture of your program’s performance. Focus on metrics such as:
- Reduced unplanned downtime (measured in hours or incidents)
- Lower emergency repair costs
- Extended equipment lifespan
- Optimized spare parts inventory
Other important indicators include team efficiency, maintenance cost savings, equipment uptime, and energy efficiency levels. For those in infrastructure or utilities, reliability metrics like the System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI) and the System Average Interruption Frequency Index (SAIFI) offer valuable insights into outage performance [7].
To stay responsive, use real-time dashboards and conduct periodic reviews. This approach allows you to adjust KPI tracking as operational conditions evolve, creating a link between immediate performance results and long-term, risk-based investment strategies.
Use Data and Predictive Models
High-quality data is the foundation of any successful predictive maintenance program. Accurate and complete data enable reliable predictions, which in turn lead to cost-effective repairs [16]. Strong data collection and management practices are critical for maximizing ROI.
Leverage tools like probabilistic modeling and advanced data analysis to simulate asset aging, predict failures, and understand energy consumption patterns. Predictive models powered by AI and machine learning are central to these efforts, though their accuracy can vary significantly – from as high as 99% to as low as 50% [15][17]. Combining structured asset data with expert insights and historical performance records helps refine these models over time, improving their reliability.
Conclusion: Putting Predictive Maintenance ROI into Action
Measuring the ROI of predictive maintenance goes far beyond crunching numbers – it’s about making informed decisions that align financial goals, risk management, and long-term sustainability. By setting a solid financial baseline, calculating both direct savings and indirect benefits, and weaving these insights into a risk-focused investment strategy, predictive maintenance evolves from being just another expense to becoming a powerful tool for asset management.
For example, a cement manufacturer achieved over $1 million in savings within just six months, delivering an impressive 57X ROI without any upfront capital investment [13]. These savings stemmed from reducing unplanned downtime by 30%, lowering maintenance costs by 25%, and extending the lifespan of critical assets.
To maintain these gains, continuous monitoring is key. Use real-time dashboards to track downtime, repair expenses, and asset longevity. High-quality data paired with predictive models ensures better accuracy, so combining structured asset information with expert insights will help fine-tune predictions over time.
Building on the ROI metrics and risk-based strategies discussed earlier, Oxand Simeo™ provides a practical framework for turning insights into actionable plans. With a database of over 10,000 aging and performance models and 30,000+ maintenance laws developed over two decades, this platform helps simulate asset behavior, prioritize investments within budget and sustainability limits, and generate ISO 55001-compliant, audit-ready plans. Organizations using this approach often see 10–25% reductions in maintenance costs for targeted areas, along with measurable CO₂ and energy savings across their portfolios.
A good starting point? Launch a pilot program focusing on your most critical assets. Gather baseline data and use the results to build a compelling business case. On average, companies see a positive ROI within 12 months, but the long-term benefits of smarter maintenance decisions continue to grow over time [5]. These steps reinforce the integrated strategy outlined earlier, helping you maximize both performance and value.
FAQs
How can I identify the most critical assets for predictive maintenance?
To pinpoint the key assets for predictive maintenance, start by zeroing in on those that play a major role in operations, have significant safety implications, or are more prone to failure. Assess each asset’s function, the potential fallout from its failure, and its historical maintenance or failure patterns.
Focus on assets that could lead to major downtime, safety hazards, or expensive repairs if they break down. By taking this focused approach, you can ensure your predictive maintenance efforts provide the most impact and align with both your operational priorities and budgetary goals.
What financial metrics should you track to calculate the ROI of predictive maintenance?
To figure out the ROI of predictive maintenance, it’s essential to focus on a few key financial metrics:
- ROI percentage: Calculate this using the formula
(Financial Benefits - Investment Costs) / Investment Costs × 100. It shows how much return you’re getting compared to what you invested. - Payback period: Measure how long it takes – typically in months – to recover your initial investment.
- Cost savings: Keep track of how much you’re saving on downtime, spare parts, and labor costs.
- Unplanned downtime costs: Evaluate the financial impact of preventing unexpected equipment failures.
- Maintenance cost reduction: Look at the percentage decrease in your total maintenance expenses.
Tracking these metrics gives you a clearer picture of the financial advantages of predictive maintenance and helps you align these benefits with your long-term investment plans.
How can I include predictive maintenance in a long-term investment plan?
To integrate predictive maintenance into a long-term investment strategy, begin by identifying key performance metrics. Focus on areas like reducing downtime, cutting maintenance costs, and extending the lifespan of your assets. Calculate the financial advantages by considering savings from lower costs, minimized risks, and prolonged asset usability. Tie these findings to your overarching goals, such as aligning with budget priorities or meeting sustainability targets. Use real-time data and measurable KPIs to track ROI consistently. This approach ensures predictive maintenance contributes to both operational efficiency and your long-term investment goals.
Related Blog Posts
- Predictive vs Reactive Maintenance: Cost Analysis Guide
- Predictive Maintenance for Asset Management (Infrastructure and Real Estate) is critical – use the web site the web site:https://theiam.org
- Predictive Maintenance & ROI
- Predictive vs. Reactive Maintenance: Which Strategy Wins for Asset Investment Planning?
