Predictive maintenance (PdM) isn’t just about preventing equipment failures – it’s a smart way to cut energy costs and reduce emissions. When machines operate inefficiently, they can consume 5% to 20% more energy than necessary. PdM uses sensors and AI to detect inefficiencies early, ensuring equipment performs optimally and maintenance happens only when needed.
Here’s why it matters:
- Energy Savings: PdM can lower energy use by 8% to 32%, particularly in systems like HVAC, compressed air, and steam.
- Cost Reduction: Maintenance costs are 20x cheaper than major upgrades, with many organizations saving millions annually.
- Emissions Impact: Cutting energy waste directly reduces CO₂ emissions, with tools like Oxand Simeo™ calculating both savings and carbon return on investment.
For example, Italian train operator Trenitalia saved $100 million annually by implementing PdM, while federal buildings cut energy use by up to 32%. These results highlight PdM’s ability to combine financial efficiency with reduced environmental impact.
The key? Start with a centralized asset inventory, use tools to simulate performance, and integrate these strategies into daily operations. PdM isn’t just maintenance – it’s a smarter way to manage energy and costs while addressing sustainability goals.
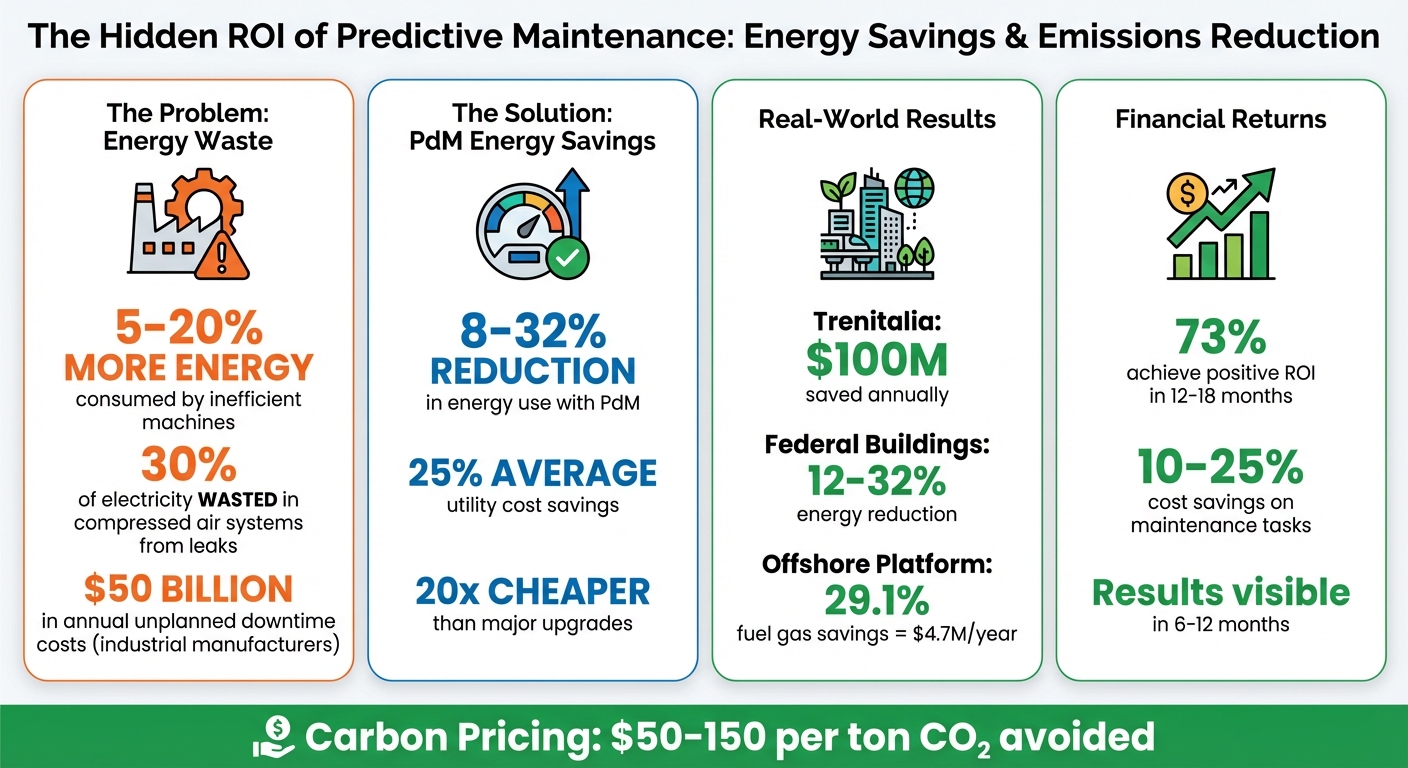
Predictive Maintenance ROI: Energy Savings and Emissions Reduction Statistics
How Predictive Maintenance Reduces Energy Use and Emissions
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a strategy that uses real-time sensor data and AI to monitor the actual performance of equipment, going beyond traditional scheduled maintenance routines. Instead of replacing components on a fixed timeline or waiting for machinery to fail, PdM analyzes condition data to predict potential failures and schedules maintenance only when necessary.
This process operates through a physical-to-digital-to-physical loop. Sensors collect physical data such as vibration, temperature, and energy consumption (Physical to Digital). AI algorithms then analyze this data to detect patterns and anomalies (Digital). Finally, the system initiates maintenance actions precisely when needed (Digital to Physical) [2]. By adopting this data-driven approach, equipment operates at optimal efficiency, avoiding unnecessary part replacements and reducing waste. This is especially crucial for tackling the energy inefficiencies often found in older equipment.
Energy and Emissions Problems in Aging Assets
Older facilities often face significant energy inefficiencies due to equipment performance issues. Over time, motors may vibrate excessively, bearings can become misaligned, HVAC filters clog, and steam traps fail. These problems force systems to work harder, consuming more energy than necessary.
PdM focuses on addressing inefficiencies in the most energy-intensive systems. For example, HVAC and ventilation systems often over-consume energy due to clogged filters or oversized motors. In compressed air systems, up to 30% of electricity is wasted pressurizing air that leaks through distribution lines [6]. Similarly, steam systems lose energy through failed steam traps and poor insulation, while electromechanical equipment experiences voltage overloads and phase imbalances, further draining power.
Specialized tools make it easier to identify and resolve these issues. Thermal cameras can detect heat from friction or leaks, sonic imagers reveal otherwise undetectable compressed air leaks, and vibration meters pinpoint bearing problems early. By addressing these hidden inefficiencies, PdM not only prevents equipment failures but also reduces energy waste. This helps organizations lower their utility costs – by an average of 25% – and achieve their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals [6].
Calculating Energy Savings and Emissions Reductions
Measuring Energy Savings with Predictive Tools
Once you’ve identified areas of energy waste, the next step is to quantify the potential savings. To do this effectively, simulation tools are essential – they model current performance and predict how different maintenance strategies might impact energy consumption.
Take Oxand Simeo™, for instance. This platform leverages a database of over 1,300 energy performance laws to analyze how energy use evolves as components age [8]. By simulating energy performance across an entire portfolio, it identifies which assets consume the most energy and suggests the best interventions. Organizations using these simulations often improve energy efficiency by 8% to 12%, simply by addressing the highest-consuming components first [10].
The tool’s multi-criteria simulations allow you to test various scenarios before making decisions. For example, you can compare whether replacing an HVAC system immediately is better than waiting two years, or if upgrading motors delivers more energy savings per dollar than repairing steam traps. This approach shifts maintenance from a reactive expense to a proactive energy management strategy.
The data generated here isn’t just about energy savings – it becomes the foundation for calculating CO₂ reductions and assessing the financial return on sustainability investments.
Tracking CO₂ Reductions and Carbon ROI
Reducing energy consumption directly translates to cutting emissions. To maximize your return on investment (ROI), it’s critical to monitor both the environmental and financial impacts. Metrics like CO₂ or kWh saved per dollar invested help quantify these benefits. When predictive maintenance enhances equipment efficiency, it not only lowers energy usage but also decreases the associated carbon emissions. Applying carbon pricing – typically between $50 and $150 per ton of CO₂ – assigns a monetary value to these avoided emissions, making it easier to link sustainability efforts to financial outcomes [11].
Oxand Simeo™ simplifies this process by integrating CO₂ reduction calculations directly into investment planning. The platform automatically generates reports aligned with ISO 55000 and CSRD/ESRS standards [7]. This makes it easier for organizations to present clear, measurable results to regulators, investors, and decision-makers.
As one Oxand client’s Chief Executive Officer noted, "We needed a tool that would allow us to consolidate the fragmented data we had and project it in a way that could be clearly presented to our elected officials, who are the decision-makers" [9].
The financial benefits of predictive maintenance often materialize quickly. In fact, 73% of implementations achieve a positive ROI within 12 to 18 months, with many organizations seeing tangible results as early as 6 to 12 months [10][9]. By tying energy savings to carbon reduction goals, you create a compelling case that links operational efficiency with broader sustainability objectives.
Automatic Machine Monitoring: Predictive Maintenance and Energy Efficiency
sbb-itb-5be7949
How to Implement Model-Driven Predictive Maintenance
Turning the concept of predictive maintenance into a practical reality takes careful planning. Start by using existing data – like maintenance logs, inspection reports, and asset records – and transform it into actionable investment strategies.
Building a Centralized Asset Inventory
The first step in any predictive maintenance plan is understanding what assets you have and their current condition. This means creating a centralized asset register that pulls together scattered data from sources like OEM manuals, maintenance records, and procurement systems. Don’t try to catalog everything at once – begin with critical assets. These are the ones whose failure could disrupt operations or lead to expensive repairs. For instance, focus on HVAC systems in hospitals, structural elements in bridges, or boilers in district heating systems.
"Setting the groundwork with a multidisciplinary team will ensure a seamless operation", says Mark Kenneday, Director of Market Strategy and Development for Healthcare at Gordian.
Involve maintenance technicians and operators in this process. Their hands-on experience with equipment quirks and failure patterns – often not documented officially – adds valuable context to historical data. You can also use Structured Facility Condition Assessments (FCA) to standardize how you collect and organize this information, ensuring consistency across all assets.
Tools like Oxand Simeo™ take this inventory to the next level. By simulating the degradation of each component over time, the platform uses inputs like equipment type, installation date, current condition, and past failure data to predict future performance. Even if some details are missing, it can still provide actionable insights. This consolidated inventory becomes the foundation for running precise, multi-criteria simulations.
Running Multi-Criteria Simulations
With your asset inventory in place, you can start testing different maintenance strategies before making major investments. Multi-criteria simulations allow you to compare various scenarios side by side. For example, should you replace an aging chiller now or wait a couple of years? Would upgrading insulation save more energy per dollar than replacing windows?
Oxand Simeo™ excels at balancing priorities like degradation risks, lifecycle costs, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions. It ranks projects by measuring Sustainability ROI, such as CO₂ or energy savings per dollar spent. Even with incomplete data, the platform can develop multi-year investment plans in just 6 to 12 weeks.
"We turned to Oxand because we needed a tool that would provide us with a predictive – not just corrective – view and help us manage our investments more effectively. Oxand stood out for its risk management capabilities", shared the Head of Budget and Asset Valuation Department at one organization [9].
These simulations also help distribute costs over time, avoiding sudden budget spikes. They ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations while guiding the smooth integration of predictive maintenance into everyday operations.
Integrating Predictive Maintenance into Operations
The final step is weaving predictive maintenance into your daily processes. Align your maintenance schedules with operational goals, sustainability targets, and regulatory demands. Start by integrating Oxand Simeo™ with your existing tools – like CMMS platforms, asset registers, and facility management systems – to consolidate data into a single, user-friendly dashboard [12].
Use the platform’s insights to plan maintenance during low-impact periods. For instance, schedule building repairs during school vacations or infrastructure upgrades during off-peak travel times. This minimizes disruptions and ensures efficient use of resources.
Tie your predictive maintenance efforts to larger sustainability goals. Oxand Simeo™ automatically generates reports that comply with ISO 55000 and CSRD/ESRS standards, simplifying regulatory requirements for decision-makers and stakeholders [7]. Within 6 to 12 months, most organizations notice measurable improvements in financial savings and operational efficiency [12].
Focus on high-impact assets – like HVAC systems, roofs, and critical infrastructure – to prevent costly emergency failures and achieve quick wins. By linking predictive maintenance to energy savings and emissions reductions, you create a powerful argument for combining operational efficiency with long-term environmental goals. Embedding these strategies into your operations not only optimizes performance but also contributes to meaningful energy and cost savings over time.
Case Studies: Energy and Emissions Results from Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance has proven its value by reducing energy consumption and emissions through proactive, data-driven approaches. These real-world examples highlight measurable results across different asset types, illustrating the shift from reactive fixes to smarter strategies.
Infrastructure Portfolios: Up to 29.1% Fuel Gas Savings
In 2022, a multinational energy operator collaborated with C3 AI to implement predictive maintenance on two turbine-driven gas compression trains at an offshore platform. Over a span of 16 weeks, historical data and 20 machine learning models were leveraged to optimize operations [13].
The system pinpointed equipment anomalies and recommended adjustments to achieve fuel gas savings of up to 29.1% per hour. This efficiency translated into an estimated $4.7 million in annual carbon tax savings for a single platform, with projections climbing to $22.2 million annually by 2030. Additionally, the platform experienced a 99% reduction in alert noise and slashed investigation times from 10 hours to just 1 hour [13].
By integrating sensor data, logs, and work orders, the system uncovered inefficiencies that manual monitoring often overlooks. The focus on high-impact assets, such as the compression trains, demonstrated how even small improvements could lead to significant energy and cost savings.
Federal Building Portfolios: 12–32% Energy Savings
Federal buildings have also seen substantial benefits from predictive maintenance. In 2023, researchers from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Carnegie Mellon University analyzed a portfolio of 550 federal buildings managed by the U.S. General Services Administration. Their study used machine learning to forecast energy retrofit impacts and identify buildings with the greatest potential for savings [4].
With tools like GSALink and targeted HVAC upgrades, the analysis revealed potential site energy savings ranging from 110 to 300 billion Btu [4]. This equated to a 12% to 32% reduction in overall energy consumption across the portfolio. The study highlighted the importance of prioritizing "high saver" buildings rather than applying uniform strategies across all assets [4].
These examples underscore the tangible benefits of predictive maintenance. By addressing inefficiencies with data-driven precision, organizations not only prevent failures but also achieve significant energy and emissions reductions. The hidden ROI of these interventions becomes clear when both energy savings and environmental impacts are quantified.
Conclusion: Maximizing ROI Through Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance plays a crucial role in eliminating inefficiencies that lead to wasted energy and unnecessary carbon emissions. When equipment operates outside its design parameters – whether due to misalignment, poor lubrication, or worn-out components – it consumes more power and generates excess emissions. Tackling these issues early not only prevents costly breakdowns but also extends the lifespan of assets, avoiding the expensive "run-to-failure" approach.
The financial benefits are just as striking. Industrial manufacturers face $50 billion in unplanned downtime costs annually [1][2], and ineffective maintenance can reduce productivity by 5% to 20% [1][2]. What’s more, maintenance and operational measures are 20 times less expensive than energy efficiency upgrades while delivering similar energy savings [3]. This makes predictive maintenance one of the smartest strategies for balancing financial goals with sustainability efforts.
Oxand Simeo™ provides the tools to make this balance achievable. With a database of over 10,000 aging models and 30,000 maintenance laws refined over two decades, the platform helps asset managers predict how components age, fail, and consume energy over time. Unlike solutions that require complex IoT sensor networks, Oxand Simeo™ works with existing data – like inspection reports, condition surveys, and historical records – to create multi-year CAPEX and OPEX plans. These plans are designed to meet budget limits while also reducing energy use and carbon emissions.
Organizations leveraging Oxand typically see 10% to 25% cost savings on targeted maintenance tasks, along with measurable reductions in CO₂ emissions and energy consumption across their asset portfolios [5][14]. By shifting from reactive to proactive, risk-based maintenance strategies, asset managers can focus on high-impact repairs, avoid unnecessary replacements, and cut down on wasted materials and supplies.
As highlighted in earlier case studies, predictive maintenance offers a clear link between operational efficiency and measurable savings. When energy savings and emissions reductions are factored into traditional cost metrics, the hidden ROI of predictive strategies becomes undeniable. With data-driven tools that align financial performance with environmental objectives, organizations can achieve a future that’s both cost-effective and environmentally responsible.
FAQs
How does predictive maintenance help lower energy use and reduce CO₂ emissions?
Predictive maintenance plays a key role in cutting down CO₂ emissions by spotting and solving equipment problems before they cause energy inefficiencies. With the help of advanced monitoring tools that track equipment performance in real time, this method ensures systems run at their best, avoiding wasted energy.
When machines operate efficiently, they consume less energy, which means fewer carbon emissions from power generation. Beyond supporting environmental goals, this proactive approach also saves money by reducing waste and increasing the lifespan of equipment.
What are the first steps to successfully implement predictive maintenance?
To kick off predictive maintenance, start by setting clear objectives and building a solid, data-driven foundation. Pinpoint the critical assets that have the greatest influence on your operations and revenue, then evaluate your current maintenance strategies, spare parts inventory, and historical failure records. Take a close look at equipment settings, control schedules, and performance metrics to identify inefficiencies or energy waste. Use these insights to establish measurable KPIs, such as energy consumption per unit produced or reductions in unexpected downtime, ensuring they align with your ROI and sustainability goals.
Once your goals are defined, prepare for accurate predictions by outfitting essential assets with IoT sensors to monitor factors like temperature, vibration, or pressure. Feed this data into an advanced analytics platform. Begin with a small pilot project to test predictive models, improve data quality, and train your team to respond effectively to alerts. Use the insights from the pilot to refine your strategy, adjust maintenance schedules based on real-time asset conditions, and scale the program across your operations. Throughout this process, monitor energy savings and emissions reductions to measure progress.
Can predictive maintenance work with my current maintenance systems and tools?
Predictive maintenance (PdM) solutions are built to work smoothly with the software and tools that most organizations already rely on, such as computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) and enterprise asset management (EAM) platforms. Through APIs and data connectors, these solutions pull data from IoT devices – like sensor readings, vibration metrics, and equipment performance stats – directly into the systems teams are already familiar with. This setup enables teams to automate alerts, plan repairs, and monitor maintenance activities without disrupting their existing workflows.
PdM platforms also integrate with current dashboards, reporting tools, and budgeting systems, preserving familiar formats such as U.S. currency ($) and date styles (e.g., December 25, 2025). By adding condition-based insights to traditional maintenance schedules, organizations can identify ways to save energy, cut emissions, and improve efficiency – all while sticking to the tools and processes they already have in place.
