Want to make smarter investment decisions for your assets? Here’s the key: Asset Investment Planning (AIP) helps you decide what to invest in, the right time to act, and how much to allocate. It’s all about using data to manage your assets effectively and aligning investments with your goals.
Key Takeaways:
- What to Invest In: Prioritize assets based on risk, impact, and alignment with business objectives.
- When to Invest: Use lifecycle stages and predictive models to time interventions efficiently.
- How Much to Invest: Focus on lifecycle costs and balance risk, returns, and long-term goals like energy savings or compliance.
By maintaining accurate asset data, assessing risks, and leveraging predictive tools, you can create a clear, data-driven plan to minimize costs and maximize performance.
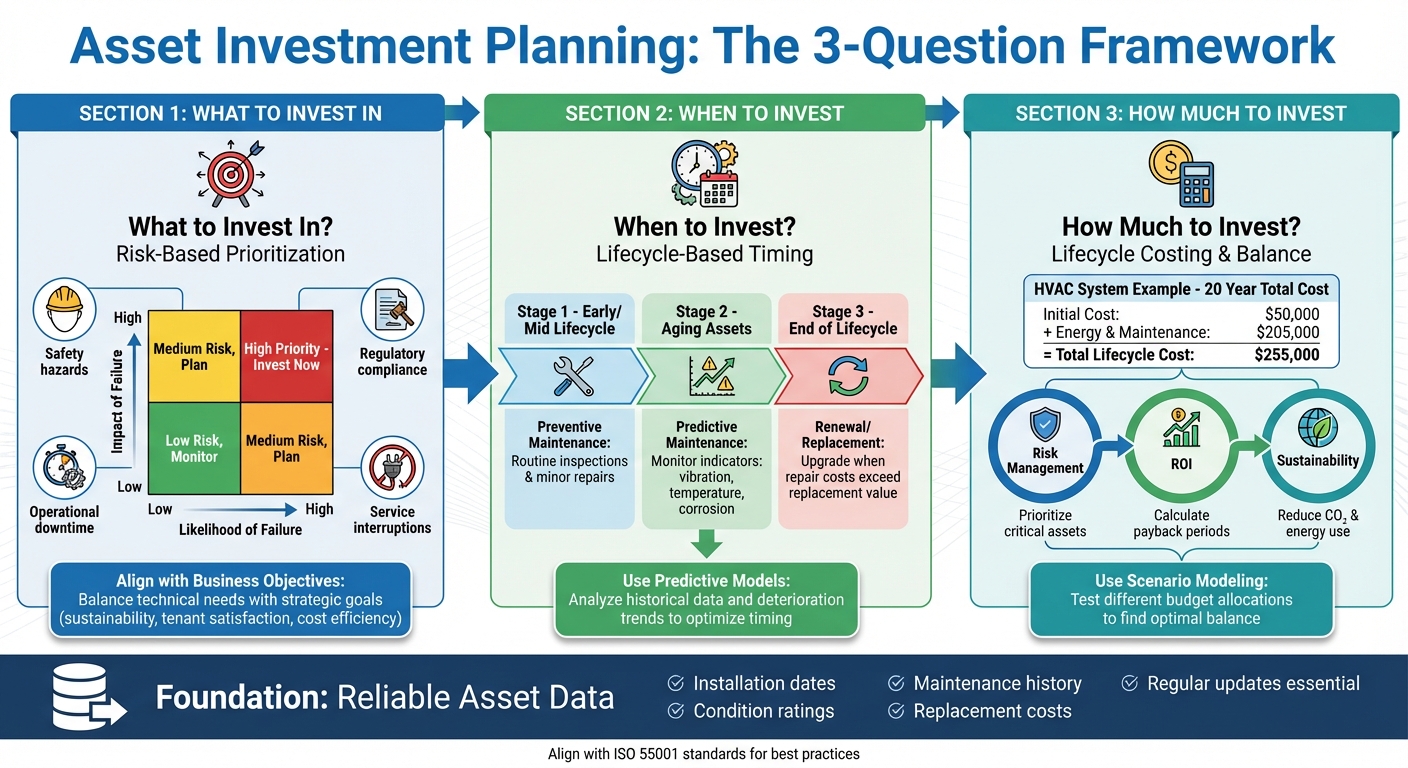
Asset Investment Planning Decision Framework: What, When, and How Much to Invest
Core Principles of Asset Investment Planning
Key Concepts and Standards
Asset Investment Planning (AIP) plays a critical role in asset management, aligning closely with the principles of ISO 55000 to guide impactful decision-making [3]. It revolves around a few essential terms: CAPEX (Capital Expenditure), which covers major investments like replacing an HVAC system; OPEX (Operating Expenditure), related to routine maintenance and repairs; and lifecycle cost, which accounts for the total expense of owning, operating, and eventually disposing of an asset.
When we talk about risk in AIP, it refers to the possibility of asset failures that could disrupt operations, jeopardize safety, or lead to regulatory penalties. The ISO 55001:2024 standard provides a structured framework for setting up, maintaining, and improving an asset management system [4]. This ensures that investment decisions are not only logical and defensible but also aligned with the overall goals of the organization.
With these foundational terms in mind, a reliable asset register becomes a cornerstone for effective planning.
Building a Reliable Asset Register
A dependable asset register is the backbone of successful Asset Investment Planning and lifecycle management. Without accurate data about your assets – such as their locations, ages, and conditions – any planning effort would be based on guesswork rather than solid evidence.
An asset register should include key details for each asset, such as the installation date, condition rating, importance to operations, estimated replacement cost, and maintenance history. This centralized database supports predictive models and risk assessments, enabling a data-driven strategy. In contrast, scattered or incomplete data makes it difficult to prioritize effectively and undermines confidence in forecasts.
Regular updates are essential. As assets age, undergo inspections, or receive maintenance, the register must reflect these changes. Using standardized forms and consistent scoring criteria helps ensure accuracy and minimizes data gaps. This disciplined approach elevates asset investment planning from a routine budgeting task to a strategic tool that safeguards long-term value.
How to Decide What to Invest In
Risk-Based Prioritization
Deciding where to allocate resources is a key challenge, especially when budgets are tight [5][6]. Organizations need a clear strategy to determine which assets to prioritize for investment.
A common approach is to evaluate the potential consequences of asset failure, factor in the likelihood of hazards occurring, and establish a baseline risk level. Investments are then selected to minimize these risks [7]. Consider the impact of potential failures, such as safety hazards, operational downtime, regulatory fines, or service interruptions.
One useful tool for this process is a risk matrix. By mapping assets based on the likelihood of failure and the severity of its impact, decision-makers can quickly spot which assets need immediate attention and which can wait.
There are two main methods for prioritization: economic evaluation and multi-criteria approaches [6]. Economic methods focus on financial returns, while multi-criteria approaches include additional factors like safety, compliance, and environmental impact. For industries like infrastructure or real estate, the multi-criteria approach often provides a broader perspective on organizational needs.
When designing a prioritization model, assign weights to criteria that align with your organization’s values. For example, a hospital might prioritize patient safety and regulatory compliance, while a commercial real estate owner might focus more on cost efficiency. The key is to make these trade-offs clear and justifiable, rather than relying on gut instincts.
This risk-based approach lays the groundwork for aligning investment decisions with broader strategic goals.
Aligning Investments with Business Objectives
After risks are assessed, it’s important to ensure investments also align with the organization’s key objectives. A high-risk asset might not always align with long-term priorities, so this step helps refine the decision-making process.
Start by translating business goals into measurable targets. For example, if tenant satisfaction is a priority, identify failures that directly affect occupant experience. If sustainability is a focus, prioritize upgrades that reduce energy use or support a shift to lower-carbon systems.
This alignment requires collaboration across teams. Asset managers bring technical knowledge about asset conditions and risks, finance teams outline budget limits and ROI expectations, and business leaders define strategic goals and acceptable service levels. When these perspectives come together, investment decisions become both practical and aligned with broader goals.
Tools like Oxand Simeo™ can assist in this process by supporting multi-criteria prioritization. This platform allows organizations to weigh factors such as risk, lifecycle costs, service levels, compliance, energy efficiency, and CO₂ impact within a single framework. Its scenario simulation feature helps visualize how different priorities – like emphasizing carbon reduction over immediate cost savings – affect the investment plan. This ensures decisions are well-informed before resources are committed.
The outcome is a ranked list of investment opportunities that balances technical needs with strategic importance. This roadmap makes it clear what requires immediate funding, what can be planned for later, and what might be deferred if circumstances remain the same.
How to Decide When to Invest
Timing Interventions Across the Asset Lifecycle
Once you’ve identified what to invest in, the next step is figuring out when. Timing is everything – intervening too soon wastes resources, while waiting too long can lead to costly failures and emergency repairs. Striking the right balance ensures maximum asset performance and budget efficiency.
The best timing depends on an asset’s stage in its lifecycle. For assets in the early to mid-lifecycle phase, preventive maintenance is key. Routine inspections and minor repairs at this stage can extend an asset’s life without breaking the bank.
As assets age and start to show signs of wear, predictive maintenance becomes a smarter option. By tracking indicators like vibration, temperature, corrosion, or visible damage, you can address issues before they escalate. This approach avoids unnecessary maintenance while catching potential failures early.
When assets near the end of their lifecycle, renewal or replacement is often the best course of action. If repair costs outweigh replacement value or newer technology offers better efficiency and savings, it’s time to upgrade. For instance, swapping out an aging HVAC system for a modern, energy-efficient model can lower operating costs and align with sustainability goals – even if the old system is still functioning.
The key is tailoring your strategy to the asset’s condition and importance. A low-risk asset might rely on preventive maintenance for years, while a critical piece of infrastructure may require predictive monitoring and earlier replacement to avoid disruptions.
To refine these lifecycle strategies, advanced tools can help pinpoint the perfect timing for interventions.
Using Predictive Models for Better Timing
Relying on fixed schedules or guesswork often leads to missteps – either unnecessary work or costly delays. Predictive models change the game by analyzing historical data, condition reports, and deterioration trends to forecast when an asset will need attention. This allows for precise scheduling: addressing issues before failures occur, but not so early that remaining useful life is wasted.
Deterioration models, for example, simulate how assets age under varying conditions. A coastal concrete structure, exposed to salt and moisture, will deteriorate faster than one located inland. By factoring in these variables, you can predict when maintenance or replacement will be required and budget accordingly.
Scenario planning adds another layer of insight. It allows you to test different timing strategies – delaying a project, accelerating another, or spreading work across budget cycles – and see how each choice impacts costs, risks, and performance.
Platforms like Oxand Simeo™ make this process even more effective. With a library of over 10,000 aging and performance models built from decades of infrastructure data, it provides detailed simulations without requiring extensive sensor networks. By using existing inspection records and condition surveys, the platform predicts how components will age and fail, helping organizations schedule interventions with precision.
The outcome? A clear, data-driven investment plan that optimizes timing and spending. This approach not only makes budgeting more predictable but also reduces emergency costs and ensures resources are used where they’ll make the biggest difference. Every dollar spent is a step toward better performance and reliability.
sbb-itb-5be7949
How to Decide How Much to Invest
Once you’ve figured out what to invest in and the right timing, the next step is deciding how much to allocate. This part of the process ties everything together – it’s about crunching the numbers and making sure your budget aligns with your goals. By combining earlier risk assessments and timing strategies with smart budgeting techniques, you can ensure every dollar is spent wisely to enhance performance and long-term value.
Lifecycle Costing and Budgeting
Budgeting isn’t just about upfront costs – it’s about the big picture. Lifecycle costing takes into account the total cost of ownership, covering everything from purchase and installation to maintenance, operation, and eventual replacement or disposal. This approach provides a full view of the financial commitment over an asset’s lifespan.
Let’s take an HVAC system as an example. While the initial cost might be $50,000, the total cost over 20 years – including energy use, maintenance, and eventual replacement – could balloon to $255,000. By analyzing both capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operating expenses, you can pinpoint where your money is going and find ways to cut costs over time.
This method also helps you compare options. Say you’re debating whether to repair an aging boiler for $15,000 or replace it with a newer, energy-efficient model for $40,000. If the new system saves $3,000 a year in energy costs and trims maintenance expenses by $1,500 annually, it could pay for itself in under six years – and continue delivering savings afterward. Lifecycle costing helps you weigh these trade-offs and make informed decisions.
Tools like Oxand Simeo™ make this process even easier. They simulate lifecycle costs and create multi-year forecasts for both CAPEX and operating expenses. By combining condition data with predictive models, platforms like this help you allocate budgets more precisely, cutting out the guesswork. Understanding lifecycle costs is key to balancing financial risks, returns, and sustainability goals.
Balancing Risk, ROI, and Sustainability
Budgeting isn’t just about cutting costs – it’s about finding the right balance between reducing risk, maximizing returns on investment (ROI), and meeting sustainability goals. The tricky part? Deciding how to prioritize these factors when resources are limited.
Risk management often takes center stage. For critical assets – like a water main or electrical substation at high risk of failure – the potential consequences can be severe. A systematic approach to budgeting starts with calculating risk as the product of failure likelihood and its impact. This helps you allocate funds to areas where the stakes are highest [1].
ROI is another big consideration. Energy-efficient upgrades, for example, can lower utility bills, while proactive maintenance can prevent costly emergency repairs. By calculating payback periods and comparing alternatives, you can ensure your funds are used where they’ll have the greatest impact.
Sustainability adds a forward-looking layer to the equation. Investments that cut energy use, lower CO₂ emissions, or align with net-zero goals might not deliver immediate financial returns, but they offer long-term benefits like better regulatory compliance and improved Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance [9]. For example, upgrading to LED lighting might cost $100,000 upfront but save $25,000 annually in energy costs while slashing carbon emissions by 50 tons per year. Over time, these savings add up while contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
The smartest investment plans use scenario modeling to test how different budget allocations affect cost, risk, and sustainability outcomes [9]. By exploring multiple scenarios, you can identify the best balance that fits your strategy and financial limits. This approach ensures your decisions are backed by data, aligned with your goals, and built to deliver both short-term and long-term success.
Implementing a Data-Driven Asset Investment Planning Process
To effectively implement asset investment planning, you need a repeatable, data-driven framework that links asset condition, risk, and cost to long-term business goals [1]. The goal is to create a continuous process for allocating capital in a way that minimizes both lifecycle costs and risks [1].
Start by aligning your strategic objectives with asset data – such as maintenance records, condition monitoring, and failure predictions – to prioritize investments [9]. Combine data from your CMMS, inspection reports, and predictive models to simulate scenarios for each asset. These simulations help you determine whether to repair, refurbish, or replace. Tools like Oxand Simeo™ can simplify this process by using asset and facilities data to prioritize investments, improve financial reporting, and boost profitability [8].
A solid process depends on reliable data and a collaborative framework that aligns with international standards like ISO 55001. This standard provides a structured way to establish and continuously refine asset management practices [10][2][11][12]. To make this work, define clear roles, set up governance structures, and commit to regular updates and reviews.
Transitioning from a reactive "fix it when it breaks" approach to a proactive strategy requires analyzing trends and deterioration patterns [8]. By comparing multiple funding scenarios – factoring in asset types, current conditions, useful life, regulations, and budgets – you can better justify funding decisions. This also helps reduce emergency repair costs while addressing sustainability and safety goals [8]. Once the framework is in place, establishing a governance model ensures alignment and ongoing improvement.
Key Steps for Implementation
Set clear objectives that align with your organization’s goals, whether it’s reducing risk, cutting costs, or meeting sustainability targets. These objectives guide investment priorities and success metrics.
Build or refine your asset register using standardized hierarchies to maintain consistency across locations. This ensures your data is reliable and actionable.
Define risk criteria based on asset condition and health data from your Asset Performance Management (APM) systems [9]. These criteria form the backbone of your prioritization framework, highlighting which assets demand immediate attention.
Develop predictive models using historical data, maintenance records, and condition assessments. These models simulate asset aging, failure rates, and energy consumption over time. With this information, you can evaluate multiple investment strategies – like automation versus traditional updates – and understand the impact of funding delays on reliability and ROI [9].
Create a multi-year plan by running scenarios that balance cost, risk reduction, and sustainability. Test different budget allocations and timelines to identify the best path forward. Your plan should be flexible enough to adapt to changes but structured enough to provide direction for the next 5 to 30 years.
Governance and Continuous Improvement
Once your investment process is up and running, governance is key to sustained success. Define clear roles for managing data, making decisions, and tracking progress. Align your governance framework with ISO 55001 to ensure a strategic and systematic approach [10][2][11][12].
Schedule regular reviews – either quarterly or annually – to update asset conditions, reassess risks, and refine your investment plan. Assets change over time, and your plan should evolve with them. Use these review cycles to validate predictive models, compare actual performance against expectations, and adjust assumptions as needed.
Collaboration across departments is essential. Investment planning benefits from input from operations, finance, sustainability, and compliance teams. Create opportunities for these groups to share insights and align priorities. This collaborative approach ensures decisions reflect the bigger picture, not just one department’s viewpoint.
Track KPIs to measure how well your plan is working. Are you reducing risk? Are lifecycle costs decreasing? Are sustainability goals being met? Use these metrics to demonstrate value to leadership and secure ongoing support for the process.
Finally, treat asset investment planning as an evolving capability, not a one-time project. As you gather more data and refine your models, the process will become more accurate and efficient. Document lessons learned, update procedures, and invest in training to build internal expertise. Organizations that commit to continuous improvement will see the greatest long-term benefits.
Conclusion
Asset investment planning isn’t a one-and-done task – it’s an ongoing process that hinges on data, connecting the dots between asset condition, risk, and costs, all while keeping your business goals in focus over time [1]. The most successful organizations treat planning as a dynamic cycle, constantly adjusting based on real-time asset insights [1][2].
At the heart of effective planning are five key elements: Planning, People, Process, Portfolio, and Performance [13]. Together, these form a framework where strategic goals align with asset data, teams collaborate with shared purpose, and decisions are both transparent and repeatable. When everyone in the organization understands how asset management choices impact broader objectives, it fosters the alignment needed to achieve sustainable, long-term success. This framework ensures clear, accountable actions throughout the entire asset lifecycle.
Strong governance is the backbone of this process. It transforms policies into consistent, auditable decisions while aligning practices with international standards like ISO 55001. This not only strengthens accountability but also builds trust with stakeholders [1][2][10]. Regular reviews – whether quarterly or annually – ensure that your plan stays relevant as assets age and conditions evolve.
Shifting from reactive maintenance to proactive investment takes dedication, but the benefits are undeniable. Beyond cost savings, it equips organizations with the ability to back funding decisions with solid data rather than relying on guesswork.
The formula is simple: start with reliable data, set clear objectives, and create a process that adapts as your assets do. The effort you put into structured planning today will safeguard the value of your assets for decades to come.
FAQs
How do I prioritize investments to align with risks and business goals?
To make smarter investment decisions, start by creating a structured approach to weigh your options. Evaluate each opportunity through the lenses of risk, cost, and expected return. Think about how these investments tie into your broader business goals – whether that’s streamlining operations, minimizing risks, or achieving sustainability targets.
Start with the essentials: prioritize investments that tackle major risks, especially those that could affect safety, compliance, or financial stability. Once those are addressed, rank other opportunities based on their ability to deliver clear, measurable benefits. This could mean cutting costs, boosting revenue, or extending the lifespan of key assets.
What are the best tools or methods for determining the right time to invest in assets?
Effective asset investment planning hinges on using tools that can evaluate the full lifecycle of assets and pinpoint the best times for investment. Many advanced systems incorporate AI-powered models and predictive analytics to examine key factors such as an asset’s age, performance patterns, and associated risks. These insights allow you to anticipate when maintenance or replacement will be necessary, ensuring that investments are both timely and cost-efficient.
By integrating these predictive tools into your strategy, you can better align your investment choices with broader objectives, such as boosting ROI, reducing exposure to risks, and meeting sustainability goals. This data-driven method helps create plans that are not only efficient but also strategically aligned with long-term success.
How do lifecycle costs impact investment decisions?
Lifecycle costs are an essential factor in making informed investment decisions. They offer a comprehensive view of an asset’s total expenses throughout its entire life – covering everything from the initial purchase price to maintenance, operational costs, and eventual disposal or replacement.
When decision-makers assess lifecycle costs, they can make smarter choices about where to allocate resources, manage budgets effectively, and prepare for long-term financial planning. This method helps ensure investments align with priorities like reducing risks, achieving the best return on investment (ROI), and meeting broader goals, including sustainability.
Related Blog Posts
- Infrastructure Asset Management: A Risk-Based Approach for Multi-Year CAPEX Planning
- End-of-Concession Management for Highways: Strategic CAPEX Planning to Meet Grantor Requirements and Ensure Profitability
- Strategic CAPEX Planning for Highway Concessions: Balancing Grantor Compliance and Profitability at End-of-Term
- Aging Infrastructure & Lifecycle Management
