Disconnected systems are costing asset managers time and money. Maintenance alone makes up over 65% of annual facility management expenses, yet most teams still operate reactively, fixing equipment only after it breaks. The problem? IoT sensors, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) often operate in silos, leaving valuable data untapped.
By integrating these systems, organizations can shift from reactive to predictive maintenance, reducing costs by 35–50% and improving asset reliability by 40–60%. This unified framework combines real-time IoT data, environmental insights from BMS, and maintenance records from CMMS, enabling smarter decisions, longer asset lifespans, and reduced downtime.
Key Benefits of Integration:
- Predictive Maintenance: Detect failures early, cut downtime by 30%, and extend asset life.
- Cost Savings: Reduce maintenance expenses by up to 50% and inventory costs by 40%.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize HVAC and lighting systems, saving 5–10% on energy use.
- Simplified Compliance: Automate reporting and ESG tracking.
The solution lies in connecting these systems through APIs, standardized data formats, and secure communication protocols. Platforms like Oxand Simeo™ centralize this data, enabling smarter investment planning and risk management. Whether managing a single building or a portfolio, integrated data transforms asset management into a proactive, data-driven process.
Difference between BMS, BAS & EMS Explained in Detail!
IoT, BMS, and CMMS: Core Data Sources for Asset Management
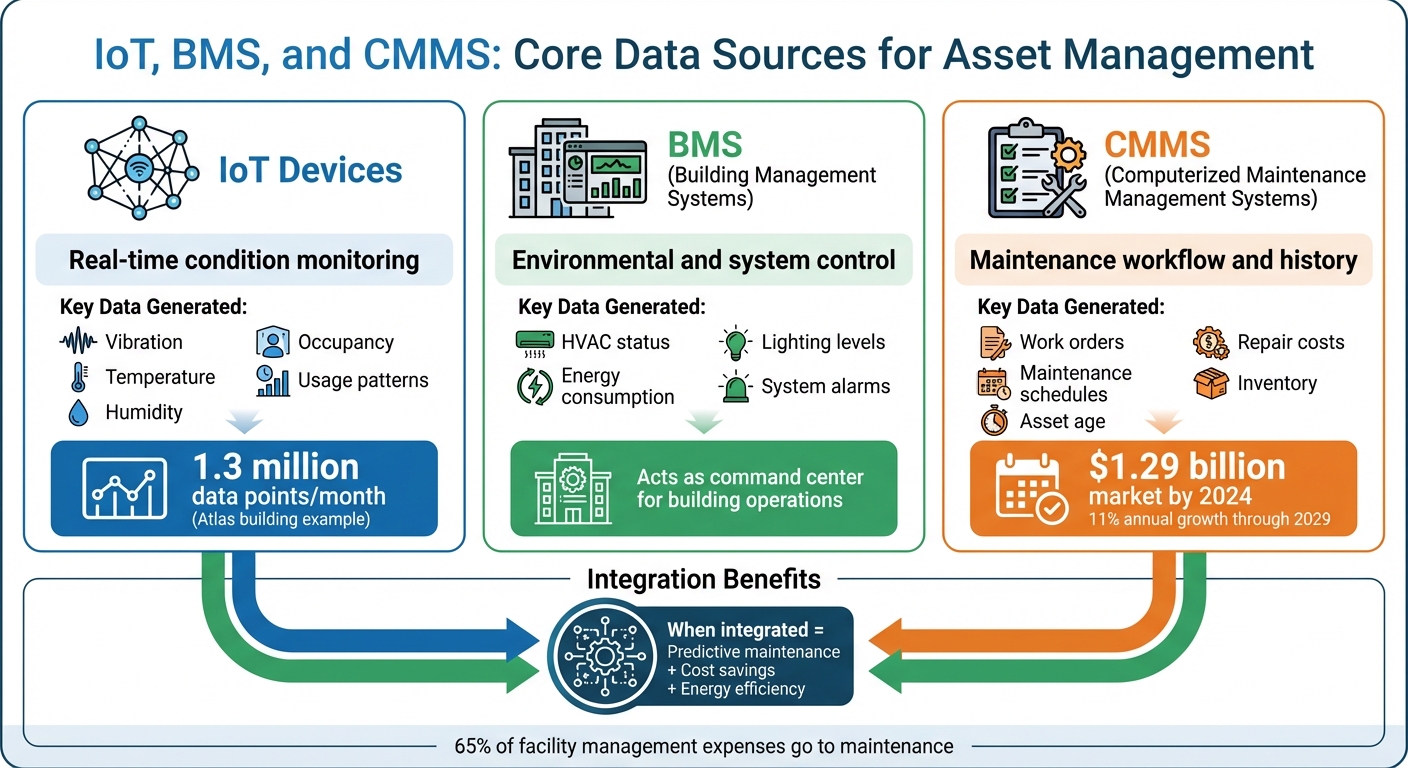
IoT, BMS, and CMMS Systems Comparison for Asset Management
IoT, BMS, and CMMS each play a distinct role in generating data crucial for integrated asset management. Understanding what each system offers is key to effectively combining their insights.
IoT Devices and Real-Time Asset Data
IoT devices are the eyes and ears of your facility, offering real-time insights into asset performance. These sensors, embedded directly into equipment, continuously monitor variables like temperature, humidity, vibration, CO₂ levels, occupancy, lighting, and energy usage patterns [1][2]. The result? A constant stream of time-stamped data that reveals how assets are functioning moment by moment.
Take, for example, a vibration sensor on a chiller. By detecting unusual patterns, it can alert maintenance teams to potential bearing wear long before a breakdown occurs. IoT data also powers Digital Twins, which are virtual models of physical assets that replicate real-world conditions, enabling better planning and problem-solving [1].
One striking example is the Atlas building at Eindhoven University of Technology. Researchers outfitted the building with IoT sensors to track metrics like occupancy, temperature, and CO₂ levels. These sensors generated over 1.3 million data points every month [1]. This massive dataset forms the backbone of advanced analytics and predictive maintenance strategies.
While IoT sensors provide granular, real-time data, they work best when paired with broader operational insights from building control systems.
Building Management Systems (BMS) for Environmental Controls
A BMS acts as the command center for a building, automating and overseeing key systems like HVAC, lighting, security, water usage, and energy distribution [1][5]. It not only collects data but also actively manages performance to ensure comfort and compliance with environmental standards.
Key data from a BMS includes HVAC performance, lighting control statuses, energy usage trends, system alarms, and operational setpoints [1][5]. This information is invaluable for identifying inefficiencies and understanding how different systems interact. However, as Wattsense points out, many traditional BMS platforms struggle to deliver real-time insights that managers need to make quick, informed decisions [5].
For example, while an IoT temperature sensor might provide a raw reading, the BMS contextualizes that data by showing whether the HVAC system is operating efficiently to maintain that temperature – and how much energy it’s consuming in the process.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) for Work Orders and History
A CMMS is the backbone of maintenance operations, keeping everything organized and on track. It manages work orders, schedules maintenance, stores historical performance data, and monitors spare parts inventory [4][2]. This system ensures workflows remain efficient and easily auditable.
The global CMMS market is projected to hit $1.29 billion by 2024, with an annual growth rate of 11% through 2029 [4]. This growth underscores the rising importance of maintenance management, especially when it accounts for over 65% of annual facility management expenses [2].
"A CMMS helps maintenance teams shift away from reactive maintenance… by automatically issuing work orders based on real-time maintenance data about an asset" [4].
For this level of automation, a CMMS needs real-time data from IoT sensors and operational context from the BMS. Without integration, it’s just a static record-keeping tool. But when these systems work together, they unlock predictive maintenance and smarter investment planning.
| System | Primary Function | Key Data Generated |
|---|---|---|
| IoT Devices | Real-time condition monitoring | Vibration, temperature, humidity, occupancy, usage patterns |
| BMS | Environmental and system control | HVAC status, energy consumption, lighting levels, system alarms |
| CMMS | Maintenance workflow and history | Work orders, maintenance schedules, asset age, repair costs, inventory |
Benefits of Combining IoT, BMS, and CMMS Data
Bringing together data from IoT sensors, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) does more than just enhance monitoring. It transforms asset management by enabling predictive maintenance, cost savings, and energy efficiency throughout an asset’s lifecycle.
Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Asset Failures
When real-time sensor data, historical records, and environmental insights come together, maintenance shifts from reactive fixes to proactive, data-driven decisions. IoT sensors continuously monitor factors like vibration, temperature, and sound. At the same time, BMS platforms track environmental conditions and system performance, while CMMS data offers historical context. This combination allows AI models to differentiate between normal operational changes and early signs of failure [6][7].
With this integration, engineers can use Advanced Troubleshooting (ATS) tools to remotely diagnose problems, reducing unnecessary site visits [7]. Maintenance work orders can be triggered before failures occur, ensuring smoother operations.
"Predictive maintenance… aims to detect incipient failures and eventual degradation based on detection of trends of component conditions using historical data so that early actions can be taken." – Jack C.P. Cheng and Qian Wang [2]
The results are impressive: predictive maintenance has been shown to cut downtime incidents by 30%, improve equipment uptime by 30% or more, and deliver an 8x return on investment over five years through reduced unplanned outages [6][8].
These predictive capabilities not only keep assets running but also lead to substantial cost reductions.
Lower Costs and Better Return on Investment
By integrating IoT and historical service data, maintenance strategies move from reactive to condition-based, reducing unnecessary repairs and extending the lifespan of components. This shift can lower labor, downtime, and parts costs by 30% [7]. Advanced Troubleshooting frameworks, which use both historical and sensor data, further cut maintenance expenses by 18% to 25% [7].
Inventory management also sees a major improvement. CMMS solutions integrated with IoT can automate spare parts tracking, leading to a 40% reduction in inventory spending [8]. This creates a single source of truth for asset data across the entire building lifecycle, minimizing redundancies and enabling remote problem-solving, which reduces field visits and labor hours.
| Maintenance Strategy | Data Source | Primary Benefit | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive (Traditional) | Scheduled intervals | Prevents some failures | High (replaces parts prematurely) |
| Condition-Based (CBM) | IoT Sensors + Analytics | Maintenance only as needed | 30% reduction in labor/parts/downtime [7] |
| Advanced Troubleshooting | Historical + Machine Data | Remote root-cause identification | 18–25% reduction in maintenance costs [7] |
| Predictive | IoT + Advanced Analytics | Early failure detection | High potential savings [7] |
However, not all implementations succeed. While 70% of traditional CMMS setups fail, those with strong integration and vendor support achieve success rates as high as 98% [8]. The key lies in proper data management and ensuring user adoption.
Beyond cutting costs, integrated data also plays a vital role in improving energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency and Carbon Reduction
Integrated data is a powerful tool for reducing energy consumption and emissions. IoT sensors and BMS platforms work together to optimize HVAC and lighting systems in real time, adjusting to occupancy and ambient conditions. Adding CMMS historical data allows machine learning models to predict equipment wear and ensure assets like chillers and boilers operate efficiently, preventing the extra energy usage caused by failing components [2][10].
"AI-based predictive maintenance provides organizations with a direct route to operational stability, extended asset life, and better resource management." – Vaneet Chathey, Technology Operations and Risk Management Leader [10]
This approach improves energy efficiency by 5% to 10% and extends equipment life by 10% to 20%, which also reduces the environmental impact of replacing assets [10][2].
Integrated systems enable Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD) tools to pinpoint energy-wasting issues in real time, even linking them to specific locations using Building Information Modeling (BIM) [1]. Digital Twin simulations further enhance efficiency by testing energy-saving scenarios virtually before making physical changes [10]. This is crucial since improperly configured BMS systems account for about 20% of building energy use, which represents roughly 8% of total U.S. energy consumption [9].
sbb-itb-5be7949
Technical Requirements for Data Integration
Bringing together IoT sensors, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) involves more than just plugging in cables. It demands a solid framework built on reliable communication protocols, standardized data formats, and secure network setups. Let’s break down the key elements that make this integration work.
APIs, Communication Protocols, and Data Exchange
To integrate data effectively, you need a mix of protocols tailored for different uses. Inside buildings, Operational Technology (OT) protocols like BACnet/SC, Modbus, and LonWorks handle local communication between devices and controllers. For cloud-based systems, IoT protocols such as MQTT v5 and OPC UA ensure efficient data transfer from sensors to centralized platforms. Meanwhile, RESTful and SOAP APIs connect CMMS platforms to IoT and BMS systems, enabling real-time data sharing and automated work orders.
Security is non-negotiable. A Zero-Trust architecture is vital, using Mutual TLS (mTLS) for device authentication, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for managing certificates, and network segmentation to separate OT zones from corporate IT systems. For critical assets, dual-path connectivity – combining fixed broadband with multi-network cellular links – ensures uninterrupted data flow.
"If it wouldn’t fly for life-safety, it isn’t good enough for building operations." – CSL Group [11]
Additionally, devices should be set up for outbound-only connections, and mTLS certificates should be automatically renewed every 90 days to maintain security.
Creating Consistent Data Structures
Different systems often label and organize data differently, which can lead to confusion. To address this, a data mapping plan is essential. This plan should define device endpoints, data formats, and transmission protocols [12]. Beyond secure communication, using standardized data formats ensures compatibility across systems. For example, consistent cost codes allow financial data from various sources to be compared seamlessly.
Semantic data models provide a practical solution for organizing data. Tagging frameworks like Project Haystack and the Brick Ontology add context to raw data, ensuring systems consistently interpret components like "temperature sensors" or "air handling units." Using Globally Unique Identifiers (GUIDs) from Building Information Modeling (BIM) or Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) ensures every asset and space has a unique identifier [1].
Organizations should also assign responsibility for specific data types to designated systems. For instance, an ERP system might manage supplier records, while a CMMS handles work orders. This creates a single source of truth and helps maintain data accuracy.
"Duplicating master records are the number-one drag on data accuracy and overall efficiency." – MaintainX Editorial Team [13]
Before implementing these changes across the board, it’s wise to test the integration in a high-impact area. This pilot phase can help identify any issues with sensor accuracy or data transmission reliability [22, 24].
Using Oxand Simeo™ to Connect and Analyze Data
Oxand Simeo™ serves as a centralized platform that integrates real-time data from IoT devices, environmental controls from BMS, and maintenance records from CMMS. It uses a model-driven approach, drawing on existing asset data and over 10,000 proprietary aging and performance models.
The platform simplifies asset analysis by offering a unified view that supports risk-based investment planning. It links operational health to financial planning, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about CAPEX and OPEX over multiple years. Users can simulate budget scenarios, explore "what if" options, and prioritize projects based on factors like risk, lifecycle costs, energy efficiency, and carbon impact. This integrated data foundation turns scattered information into actionable insights for proactive decision-making.
Importantly, Simeo™ doesn’t replace your current systems. Instead, it connects to them through open APIs and standard protocols, consolidating fragmented data into a single, cohesive investment plan. Whether your organization uses extensive IoT coverage or relies on periodic inspections, the platform adjusts to your data environment, helping you make smarter, more strategic investment decisions.
Practical Applications of Integrated Asset Data
Automated Maintenance Triggers and Scenario Planning
IoT sensors that monitor factors like vibration, temperature, or pressure can automatically create work orders in a CMMS, cutting out the need for manual input. For example, researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology implemented this method across four chillers in three academic buildings starting in April 2020. By integrating BIM, BACnet-based IoT networks, and facility management systems, they used ANN and SVM algorithms to predict component conditions. This allowed for preemptive maintenance and streamlined material procurement [2].
Integrated asset data also enhances scenario planning, making it possible to test various investment strategies before committing resources. Imagine comparing the outcomes of replacing a chiller now versus waiting two years or evaluating how different budget levels impact overall risk across a portfolio. This kind of analysis helps optimize replacement planning while accounting for real-world factors like funding, staffing, and compliance deadlines. The result? Timely maintenance that not only keeps operations smooth but also informs broader risk assessments for your portfolio.
Portfolio-Level Risk Assessment and Compliance
Having a unified view of asset health, risk, and compliance makes it easier to prioritize maintenance based on factors like condition, criticality, and the likelihood of failure. One example is a multi-story academic facility where an integrated system combined BMS data with BIM models. This setup supported real-time 3D visualizations and automated fault detection, offering a clear picture of asset performance.
This same integration simplifies regulatory reporting. Instead of pulling data manually from different systems, automated platforms can generate audit trails that document all maintenance activities. For organizations focused on carbon reduction targets, the same data framework can also support ESG reporting by linking energy use, emissions, and asset performance into one cohesive view.
Results Achieved with Oxand Simeo™
Organizations leveraging Oxand Simeo™ to analyze data from IoT, BMS, and CMMS systems often see 10–25% cost savings on targeted maintenance tasks. By combining real-time condition monitoring with over 10,000 proprietary aging models and 30,000+ maintenance regulations, the platform helps extend asset lifespans and reduce overall ownership costs. Infrastructure managers can delay costly replacements by accurately predicting how much useful life remains for critical components.
The platform also delivers notable sustainability gains. Clients report measurable reductions in CO₂ emissions and energy use across their portfolios by optimizing maintenance schedules and identifying underperforming assets for replacement. Simeo™ connects operational health data with financial planning, enabling users to simulate budget scenarios that balance risk, lifecycle costs, and environmental impact. Plus, it’s accessible even if you don’t have an advanced IoT sensor setup – Simeo™ works with existing surveys, inspections, and available data, making it a practical choice regardless of your current digital infrastructure.
Conclusion
Bringing together IoT, BMS, and CMMS data breaks down the silos that often hide critical insights about asset performance. When these systems operate as a unified whole, it shifts organizations from merely reacting to problems toward making proactive, data-informed decisions. The payoff? Fewer unexpected breakdowns, reduced maintenance expenses, and smoother operations overall. In fact, companies that embrace this approach have reported up to 30% reductions in maintenance costs [15], energy savings ranging from 8% to 20% within the first year [11], and workforce productivity improvements of 13% [14].
Oxand Simeo™ takes this concept further by combining real-time operational data with proprietary models. This allows for the creation of multi-year CAPEX and OPEX plans that carefully balance risk, budget constraints, and carbon reduction goals. These enhancements pave the way for even more advanced integration solutions.
Transitioning from the isolated systems of Industry 3.0 to the interconnected environment of Industry 4.0 isn’t just about adopting new technology. It’s about extending the lifespan of assets, avoiding expensive replacements, and making smarter investment decisions – even when budgets are tight [15]. With integrated data, you can simulate budget scenarios, focus on high-risk assets, and produce audit-ready reports that meet both regulatory requirements and ESG objectives. This comprehensive approach transforms asset management from short-term fixes to long-term, strategic planning.
Whether you’re overseeing a single building or a large portfolio, the direction is clear: connect your data, assess your risks, and plan with precision. Dean Stanberry, Chairman of IFMA Global Board of Directors, captures the importance of this shift perfectly:
"AEC owns a project for 18–36 months, but Operations deals with it for the next 75–100 years" [3].
The decisions you make today, driven by integrated data and analytics, will shape your assets’ performance and sustainability for generations to come.
FAQs
How does combining IoT, BMS, and CMMS data enhance predictive maintenance?
Integrating information from IoT sensors, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) offers a complete picture of how assets are performing. This combination of data paves the way for advanced analytics and machine learning to identify early signs of equipment wear, predict failures, and fine-tune maintenance schedules.
By tackling issues before they escalate into major problems, this method minimizes unexpected downtime, prolongs the life of assets, and boosts overall efficiency. It also empowers organizations to make smarter, more strategic decisions, cutting costs while enhancing operational reliability.
What are the essential technical requirements for integrating IoT, BMS, and CMMS data?
To integrate IoT devices, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) effectively, these systems need to work together seamlessly, remain secure, and be able to grow with your needs. Start by ensuring they use standardized interfaces such as APIs or open data models. These tools enable smooth communication between systems. Additionally, compatibility is a must – IoT sensors, BMS, and CMMS should support widely used communication protocols like MQTT, BACnet, or Modbus. Reliable connectivity, whether through wired or wireless networks, and a robust data infrastructure, such as cloud or on-premise storage, are essential for handling high-speed data effectively.
Security is another critical piece of the puzzle. Protect sensitive data with end-to-end encryption, authentication measures, and role-based access controls. Adhering to established industry standards like ISO 27001 or NIST 800-53 can help ensure compliance and strengthen cybersecurity. Keep the "5 C’s" of IoT in mind – connectivity, continuity, compliance, coexistence, and cybersecurity – to maintain both reliability and trust in your systems.
Finally, a strong focus on data is crucial. Utilize real-time data pipelines, scalable storage solutions, and advanced analytics tools like AI and machine learning. This approach turns raw data into actionable insights, enabling predictive maintenance and automating workflows within the CMMS. The result? Smarter decisions and greater operational efficiency.
How does Oxand Simeo™ improve asset management and cut costs?
Oxand Simeo™ integrates data from IoT devices, Building Management Systems (BMS), and Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) into a single, cloud-based platform. By breaking down data silos, it delivers real-time insights into asset performance and automates maintenance schedules based on risk. This proactive approach helps prevent expensive failures and can cut unplanned downtime by as much as 90%.
Simeo links maintenance tasks directly to asset performance metrics, streamlining inventory management and reducing excess stock. It also pinpoints high-return investment opportunities, empowering smarter decisions that boost ROI, extend the lifespan of assets, and lower carbon emissions. In essence, Simeo turns scattered data into actionable insights, driving cost efficiency and enhancing reliability across your entire asset portfolio.
Related Blog Posts
- Predictive Maintenance for Asset Management (Infrastructure and Real Estate) is critical – use the web site the web site:https://theiam.org
- How predictive maintenance (without IOT and real time) brings value to infrastructure and building asset owners
- Sustainability & Carbon Reduction Solutions
- Energy Savings and Emissions Reduction: The Hidden ROI of Predictive Maintenance