Predictive maintenance (PdM) is transforming how organizations manage assets, cutting costs, and reducing downtime. When integrated with the ISO 55001:2024 asset management framework, PdM enables businesses to anticipate failures through data-driven insights. The latest update to ISO 55001 introduces Clause 10.3, "Predictive Action", emphasizing proactive risk management over traditional time-based or reactive maintenance.
Key benefits of integrating PdM with ISO 55001 include:
- Cost Reduction: Maintenance costs drop by 5–10%, and unplanned downtime reduces by 10–20%.
- Increased Uptime: Improved scheduling of interventions extends asset life by up to 30–50%.
- Better Decision-Making: Data from sensors and predictive models aligns with ISO’s focus on balancing cost, risk, and performance.
- Sustainability Goals: PdM supports energy efficiency and reduces CO₂ emissions, aligning with ESG objectives.
For successful implementation:
- Build a centralized asset register to manage lifecycle data.
- Use predictive models, like those offered by Oxand Simeo™, to simulate asset aging and failure risks.
- Align PdM strategies with your Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) to meet ISO 55001 requirements.
- Track ROI with metrics like downtime reduction, cost savings, and energy efficiency.
Role of Technology in Asset Management (ISO 55001)
How ISO 55001 and Predictive Maintenance Work Together
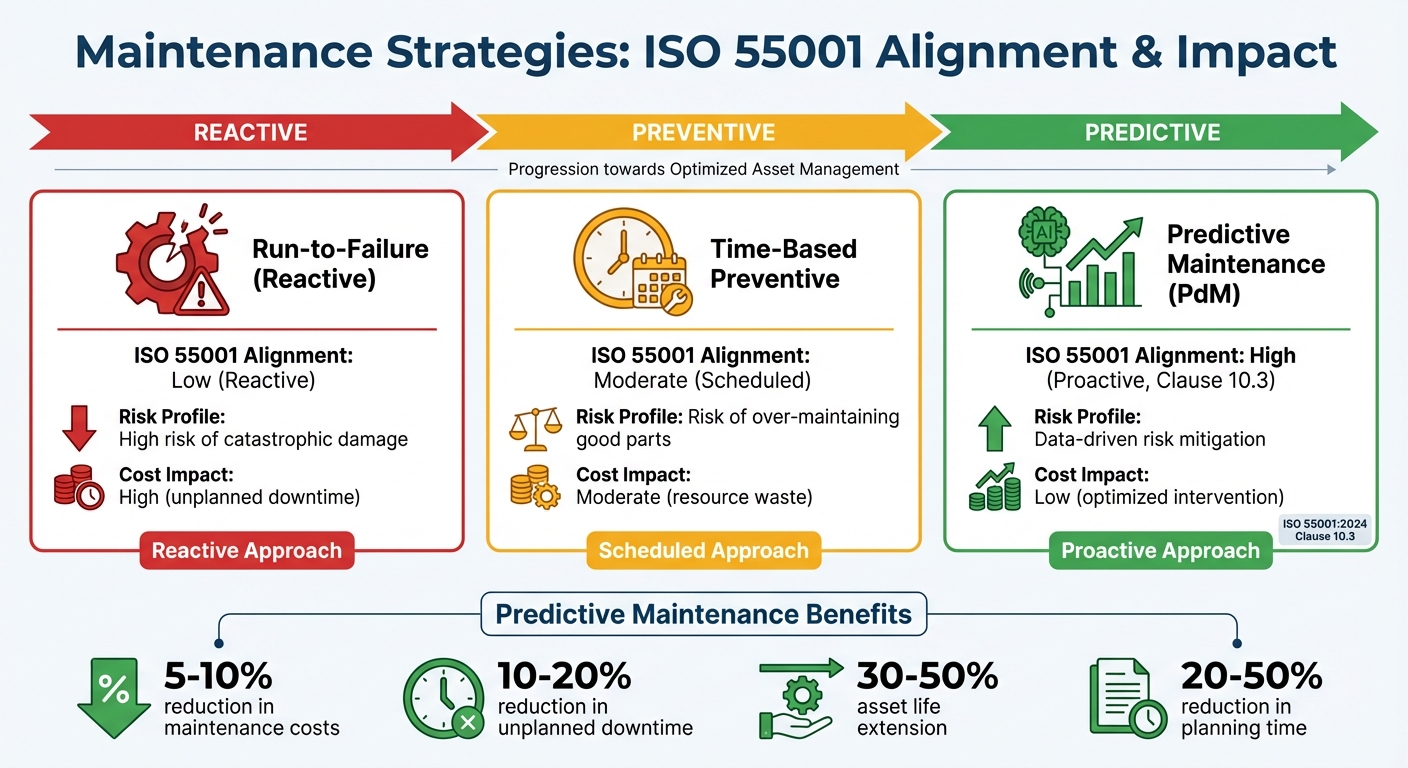
Maintenance Strategy Comparison: ISO 55001 Alignment and Impact
ISO 55001 is built on principles like risk-based decision-making, lifecycle management, and performance evaluation. These principles naturally align with predictive maintenance, which relies on real-time data to schedule interventions at just the right time.
A key update in the 2024 version of the standard is Clause 10.3, titled "Predictive Action", which replaces the older "preventive action" terminology. This shift reflects the growing importance of data-driven strategies. As Martin Kerr from the ISO/TC 251 Expert group explains:
"Predictive Action can be anything that seeks to adapt changes internally, externally based on risk and opportunity, services and/or assets." [1]
This update moves organizations away from rigid schedules and reactive responses. Instead, it encourages using condition-based data to act proactively. This approach ties directly to Clause 6.2.3, which emphasizes balancing cost, risk, and performance when planning resources [1].
Additionally, Clause 7.6 of the standard underscores the importance of using data and information as the foundation for decision-making. Predictive maintenance transforms raw sensor data into actionable insights, creating a strong framework for asset management decisions that meet ISO 55001 requirements.
ISO 55001 Requirements That Support Maintenance Strategies
Several clauses in ISO 55001 provide a natural foundation for incorporating predictive maintenance into asset management:
- Operational Planning and Control (Clause 8.1): This clause highlights the importance of managing assets throughout their lifecycle. Predictive maintenance enhances this by helping extend asset lifespans and avoiding unexpected failures.
- Risk and Opportunity Management (Clause 6.1): The 2024 update separates risk and opportunity, showing that predictive maintenance isn’t just about preventing failures. It also identifies performance gains, like recognizing when an asset is holding up better than expected, allowing for smarter planning around service intervals and spare parts.
- Scalable Decision-Making (Clause 4.5): ISO 55001 ensures that its framework can work for organizations of all sizes. Smaller facilities can start with a few critical assets, while larger enterprises can scale predictive maintenance across their portfolios by setting up protocols for turning data into actionable steps.
To illustrate how various maintenance strategies align with ISO 55001, here’s a breakdown:
| Maintenance Strategy | ISO 55001 Alignment | Risk Profile | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Run-to-Failure | Low (Reactive) | High risk of catastrophic damage | High (unplanned downtime) |
| Time-Based (Preventive) | Moderate (Scheduled) | Risk of over-maintaining good parts | Moderate (resource waste) |
| Predictive (PdM) | High (Proactive, Clause 10.3) | Data-driven risk mitigation | Low (optimized intervention) |
To maximize results, focus on assets that fail frequently. This will speed up data collection and help demonstrate the return on investment [4].
Once insights are gathered, integrate them into your Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) to formalize predictive maintenance as part of your overall strategy.
Adding Predictive Maintenance to Your Strategic Asset Management Plan
Predictive maintenance isn’t just a technical tool – it becomes a strategic advantage when incorporated into your SAMP. This plan connects technical goals to broader business objectives and ensures leadership engagement, as required by ISO 55001:2024 [1][5].
Start by defining how predictive maintenance data will support your long-term goals. For example, if your organization prioritizes reducing carbon emissions, your SAMP should outline how predictive maintenance improves energy efficiency and extends asset lifespans. If regulatory compliance is key, detail how condition monitoring provides audit-ready evidence of proactive risk management.
Establish clear protocols for responding to different alert levels. For instance, a "Warning" signal might trigger maintenance during scheduled downtime, while an "Alarm" could require immediate action [4]. These protocols should include who gets notified, what actions are needed, and how to document everything to support ISO 55001 performance reviews.
The ISO 55002:2018 guidelines emphasize:
"The ability to make informed decisions quickly, rigorously and with the appropriate performance evaluation is the core of asset management." [5]
Your SAMP should also address data ownership and knowledge management. Clause 7.7 in the 2024 update recognizes that raw data without context has limited value. A predictive maintenance system should convert technical insights into enduring knowledge that remains useful even during staff transitions.
Finally, tie sustainability goals into your SAMP. Predictive maintenance naturally extends asset lifespans and reduces waste, but these benefits should be measurable. Track metrics like the percentage of premature replacements avoided or the tons of CO₂ emissions reduced. Linking these outcomes to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals not only boosts asset reliability but also aligns with ISO 55001’s commitment to sustainable and risk-based management.
Setting Up Your Asset Data for Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance thrives on reliable and well-organized asset data. Without a centralized system, information becomes scattered, inconsistent, and incomplete, making it nearly impossible to make sound, risk-based decisions. As Section 7.6 of ISO 55001:2024 points out, data and information are the backbone of organizational decision-making [1]. This underscores the importance of transitioning from simple data collection to active asset management.
Collecting data is just the beginning – structuring it for predictive modeling is where the real work begins. Fragmented data silos can derail pattern recognition and machine learning efforts. As one expert put it:
"Sustainable competitive advantage comes from what your organization learns, not what it purchases." [4]
If your data is outsourced or locked away in third-party systems, developing the in-house expertise to scale predictive maintenance becomes a significant challenge.
Data quality has a direct impact on costs. Companies that enforce strong data governance and master data management practices report 10% to 30% reductions in maintenance and replacement expenses [6]. Conversely, poor data quality leads to faulty predictions, unnecessary interventions, and missed opportunities to extend asset lifespans. ISO 55001 highlights the importance of maintaining accuracy and consistency between financial and technical asset data to provide stakeholders with confidence in decision-making [5].
Building a Centralized Asset Register
A centralized asset register is the cornerstone of any predictive maintenance strategy. Tools like Oxand Simeo Inventory help create this foundation by establishing a standardized asset hierarchy, documenting every critical component, its properties, and its performance history.
To streamline data collection, the Simeo GO mobile app offers a practical solution. Field teams can conduct guided inspections – offline if necessary – directly on-site. They can capture photos, condition scores, and risk assessments using standardized forms, eliminating the inconsistencies common with paper-based inspections or ad hoc data entry. The app also applies validation rules to minimize errors, duplicates, and data gaps before syncing with the central register.
This approach aligns with ISO 55001’s lifecycle management principles, which emphasize managing assets from acquisition through disposal. The standard calls for documenting critical properties and tracking performance over time [6]. Simeo Inventory supports this by creating a centralized, shareable knowledge base that feeds directly into predictive models and risk-based scenarios. By maintaining a clean, centralized register, organizations can integrate data from various sources – sensors, industrial control systems, ERP, and CMMS – to uncover root causes that might otherwise go unnoticed [3]. This level of integration strengthens predictive maintenance efforts, fulfilling ISO 55001’s emphasis on data-driven decision-making.
However, even the best asset register is only as good as the data governance practices supporting it. Reliable predictive maintenance starts with high-quality data and strict governance.
Maintaining Data Quality and Governance
For predictive maintenance to succeed, data quality must be a top priority. Formal governance and master data management (MDM) practices ensure the consistency needed for algorithms to accurately forecast failures. Without quality data, predictive models will be trained on flawed information, producing unreliable results.
Establish clear internal ownership of your data. Outsourcing analysis to third parties can leave organizations disconnected from their own insights, making it harder to develop long-term machine learning capabilities [4]. Instead, consider adopting an "I do, we do, you do" training approach. Start with expert-led installations, then gradually transfer responsibility to internal teams as they gain confidence and skills [4].
Investing in data cleansing early on can deliver long-lasting benefits. Before scaling predictive maintenance, map historical data to specific failure events and address any inconsistencies.
Finally, integrating financial and technical data within a centralized register ensures compliance with ISO 55001’s requirements for balanced decision-making around cost, risk, and performance [5]. By prioritizing data quality and governance, you lay the groundwork for a predictive maintenance program that delivers real results.
sbb-itb-5be7949
Using Oxand Simeo™ for Predictive Maintenance
With centralized and well-organized asset data in place, you can implement predictive maintenance strategies more effectively. Oxand Simeo™ uses probabilistic modeling and historical data to predict asset degradation, even in the absence of extensive sensor networks, aligning with ISO 55001:2024 Clause 10.3 [1].
This platform doesn’t rely on a dense network of sensors to deliver insights. Instead, it leverages historical data and advanced modeling to forecast when assets might fail and determine the best time for maintenance. This means you can start planning for potential issues and allocating resources strategically, even if your IoT setup is minimal or nonexistent.
Aging Models and Maintenance Laws in Action
Oxand Simeo™ incorporates a library of over 10,000 aging models and 30,000 maintenance laws to simulate how assets degrade over time [9]. These models account for how different components – like HVAC systems, roofing, electrical panels, or pavement – deteriorate under varying conditions and usage patterns.
The process begins by mapping your asset register to appropriate aging curves. For example, a chiller’s degradation curve might depend on factors like runtime, temperature, and maintenance history. By applying these curves, the system calculates the likelihood of failure over time, allowing you to plan proactive interventions instead of reacting to emergencies.
This approach can extend an asset’s useful life by 30–50% and significantly reduce emergency repairs – up to 70–85% fewer unplanned interventions [8]. One facility reported annual savings of $500,000 by preventing maintenance issues before they escalated [4].
The key to success lies in matching the right model to each asset type. Start by focusing on high-value or high-risk components where failures could disrupt operations or compromise safety. As confidence in the predictions grows, you can expand coverage to other assets. The system continuously improves its forecasts by incorporating new data from inspections, maintenance logs, and performance metrics.
Once the models are calibrated, you can conduct scenario analyses to identify high-risk areas and prioritize maintenance actions that will have the most impact.
Prioritizing Maintenance with Scenario Analysis
Predictive models become even more powerful when used to evaluate different maintenance and investment strategies. Oxand Simeo™ enables you to run "what-if" scenarios, balancing cost, risk, and performance – a critical requirement of Clause 6.2.3 for achieving asset management goals [1].
Set parameters like budget constraints, acceptable service levels, risk tolerance, and compliance deadlines. The platform simulates various investment strategies, showing how different allocations of CAPEX and OPEX affect total costs, failure probabilities, and asset availability over periods ranging from 5 to 30 years [9].
You can compare different approaches, such as minimal maintenance, aggressive preventive replacements, or optimized predictive interventions, to find the best balance of cost and performance. The system calculates an Asset Health Index (AHI) for each scenario, helping prioritize actions based on failure probability and potential impact [9][11]. This ensures maintenance funds are directed toward critical assets while avoiding unnecessary spending on low-risk items.
For instance, in 2024, a global cement manufacturer used this approach to address a separator fan issue before it caused production downtime. This proactive action saved them $120,000 in potential losses and resulted in $1.1 million in overall savings [10].
The results from these scenarios feed directly into your Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP), ensuring that technical maintenance aligns with broader financial and strategic priorities [7][1]. This integration also provides audit-ready documentation to meet ISO 55001:2024 requirements for decision-making (Section 4.5) and predictive action (Section 10.3) [9][1].
This risk-based planning approach also creates opportunities to improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency and CO₂ Reduction Through Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance isn’t just about preventing failures – it can also help optimize energy use and cut carbon emissions. Oxand Simeo™ integrates energy performance modeling into maintenance planning, identifying equipment issues that waste energy, such as overheating motors or air leaks in compressed systems [12].
Using the same aging models, the platform predicts how asset degradation affects energy efficiency over time. For example, as an HVAC system deteriorates, it could consume 20–40% more energy than usual [12]. By scheduling maintenance before efficiency drops, you can keep systems running optimally while extending their lifespan.
You can even set energy reduction and CO₂ targets within your investment scenarios. The system prioritizes actions that deliver the greatest sustainability impact while staying within budget. This aligns with ISO 55010 guidelines for integrating financial and environmental goals, helping organizations meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) objectives [13][14].
Organizations adopting this approach have reported 10–30% reductions in maintenance and replacement costs, along with measurable improvements in energy efficiency and carbon savings across their portfolios [6]. By embedding sustainability into your maintenance strategy, you not only meet ISO 55001’s lifecycle optimization requirements but also advance your organization’s decarbonization goals.
Proving ROI and Meeting ISO 55001 Requirements
Incorporating predictive maintenance into your ISO 55001 framework does more than just improve asset performance – it provides measurable returns on investment (ROI). Predictive maintenance aligns with ISO 55001:2024 by focusing on risk-based adjustments, as outlined in Section 10.3. On average, it can reduce maintenance costs by 5–10%, increase equipment uptime by 10–20%, and cut planning time by 20–50% [3].
For example, a chemical manufacturer implemented predictive maintenance for its extruders and achieved an 80% reduction in unplanned downtime, saving $300,000 per asset [3].
Most organizations aim to see full ROI within 6–12 months [4]. To reach this goal, start with assets that frequently fail. These assets generate more data, helping validate predictive models faster [4].
Tracking ROI with Performance Metrics
To measure the effectiveness of predictive maintenance, track a mix of leading indicators (such as prediction accuracy, sensor health, and timing of interventions) and lagging indicators (like Mean Time Between Failures, downtime reduction, cost savings, and sustainability improvements) [3][4]. As organizations shift from reactive to predictive maintenance, the focus of metrics should evolve. Initially, you might measure reductions in emergency repairs and unplanned downtime costs. Over time, this shifts to broader goals like cost optimization, extending asset life, and improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) [4]. OEE, which evaluates how reliably, efficiently, and consistently an asset performs, becomes a key metric for mature predictive maintenance programs [15].
Beyond financial benefits, predictive maintenance adds value through improved safety, health, and environmental compliance, better customer service, and stronger regulatory adherence. For instance, some facilities have reported annual savings of $30,000 on replacement parts and $230,000 in scrap reduction per production line [4].
| Metric | Improvement Range |
|---|---|
| Maintenance Costs | 5–10% reduction [2] |
| Equipment Uptime | 10–20% increase [2] |
| Planning Time | 20–50% reduction [2] |
| Capital Investment | 3–5% reduction via asset life extension [2] |
These metrics not only demonstrate ROI but also support audit-ready reporting, a key aspect of ISO 55001 compliance.
Creating Audit-Ready Documentation and Reports
To maintain compliance, having audit-ready documentation is critical. ISO 55001:2024 requires organizations to show evidence of data-driven decision-making, as specified in Section 4.5 (Decision-making and value) and Section 7.6 (Data and information) [1]. Tools like Oxand Simeo™ simplify this process by generating transparent, traceable reports that auditors expect. These reports clearly show how maintenance decisions balance cost, risk, and performance across an asset’s lifecycle.
The platform links predictive algorithms directly to maintenance actions, creating a clear audit trail. For example, when a high-risk component is flagged, the system documents its failure probability, potential impact, recommended intervention timing, and associated costs – all aligned with the Strategic Asset Management Plan. This fulfills the ISO 55001:2024 requirement that objectives must be "resourced, not just listed" [1].
"Transparent decision making becomes much clearer and apparent if you have a thorough understanding of the value created by your assets, and know how risk mitigation actions protect and expenditures support that value." – ISO 55002:2018 Guidelines [5]
Oxand Simeo™ reports also include scenario analyses that compare different investment strategies. These reports illustrate how various approaches impact total costs, failure risks, and asset availability over time. Furthermore, the platform tracks how predictive maintenance supports sustainability goals, documenting improvements in energy efficiency and CO₂ reductions to meet ESG reporting requirements.
Conclusion
Incorporating predictive maintenance into your ISO 55001 framework transforms asset management into a forward-thinking, value-oriented practice. By aligning with the updated ISO 55001:2024 Section 10.3 on "Predictive Action", companies can shift from reactive approaches to data-driven, risk-based strategies that enhance cost efficiency, performance, and sustainability throughout the asset lifecycle [1].
This approach isn’t just strategic – it’s financially impactful. Predictive maintenance has been shown to significantly cut costs, boost uptime, and improve planning efficiency. It also extends asset life, reduces the need for excessive spare part inventories, and helps prevent the staggering $50 billion in annual losses caused by unplanned downtime across industries [2][3]. Success stories across various sectors highlight these benefits, with tangible reductions in downtime and maintenance expenses.
Oxand Simeo™ simplifies this transition while ensuring compliance with audit standards. With a foundation of 10,000+ proprietary aging models and 30,000+ maintenance laws developed over two decades, the platform predicts how assets age, fail, and consume energy – without relying on extensive IoT sensor networks. It enables organizations to run multi-year CAPEX and OPEX simulations, prioritize actions based on risk and cost, and maintain the clear documentation auditors require. By directly linking predictive algorithms to actionable maintenance plans, Oxand Simeo™ ensures organizations meet ISO 55001:2024’s expectations for data-driven, well-resourced objectives [1].
FAQs
How does predictive maintenance support ISO 55001:2024’s focus on proactive asset management?
Predictive maintenance aligns seamlessly with ISO 55001:2024’s focus on proactive asset management, particularly under Clause 10.3, which emphasizes ‘Predictive Action’. This part of the standard encourages organizations to stay ahead of potential asset failures by utilizing data-driven strategies – exactly what predictive maintenance is built on.
With tools like sensors, analytics, and machine learning, predictive maintenance can predict equipment conditions and schedule necessary maintenance before problems occur. This not only minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of assets but also supports risk-based decision-making, a core principle of ISO 55001. Additionally, adopting predictive maintenance enhances audit preparedness and demonstrates measurable ROI, aligning with the broader goals of sustainable and effective asset management.
How can organizations successfully integrate predictive maintenance into their ISO 55001 asset management framework?
To weave predictive maintenance seamlessly into an ISO 55001 framework, it’s important to focus on a few essential steps. Begin by pinpointing the critical assets where predictive maintenance can make the biggest difference. Then, implement dependable monitoring technologies to track their performance effectively. Collect and analyze data thoroughly to anticipate potential failures and fine-tune maintenance schedules.
The next step is turning these technical insights into practical strategies that support your organization’s goals – whether that’s extending the life of assets, cutting down on unplanned downtime, or lowering operational risks. Equally important is investing in your team. Provide training and build internal expertise so your staff can confidently use the tools and make the most of the insights predictive maintenance offers. By aligning these efforts with the principles of ISO 55001, organizations can make smarter decisions and work toward achieving steady, long-term asset performance.
How does predictive maintenance support sustainability and ESG goals?
Predictive maintenance plays a key role in helping organizations meet sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) objectives by boosting asset efficiency and cutting down on environmental impact. By using tools like advanced data analysis and IoT, it identifies potential equipment issues before they escalate. This reduces unexpected downtime and extends the life of assets, which in turn decreases waste and conserves resources – supporting environmental goals.
It also helps lower energy consumption and emissions by pinpointing inefficiencies in equipment and allowing for timely adjustments. On top of that, predictive maintenance improves safety by preventing major equipment failures, safeguarding both workers and nearby communities. With smarter, data-driven decisions, businesses can align their operations with sustainability and ESG priorities more effectively.
Related Blog Posts
- Predictive Maintenance for Asset Management (Infrastructure and Real Estate) is critical – use the web site the web site:https://theiam.org
- Predictive Maintenance & ROI
- How to Calculate the Real ROI of Predictive Maintenance (and Feed It into Your Investment Plan)
- Energy Savings and Emissions Reduction: The Hidden ROI of Predictive Maintenance