Managing infrastructure without a unified data system is expensive and inefficient. Key data often lives in disconnected systems, leading to higher costs, unplanned downtime, and poor investment decisions. But integrating historical and real-time data can transform maintenance and planning strategies. Here’s how:
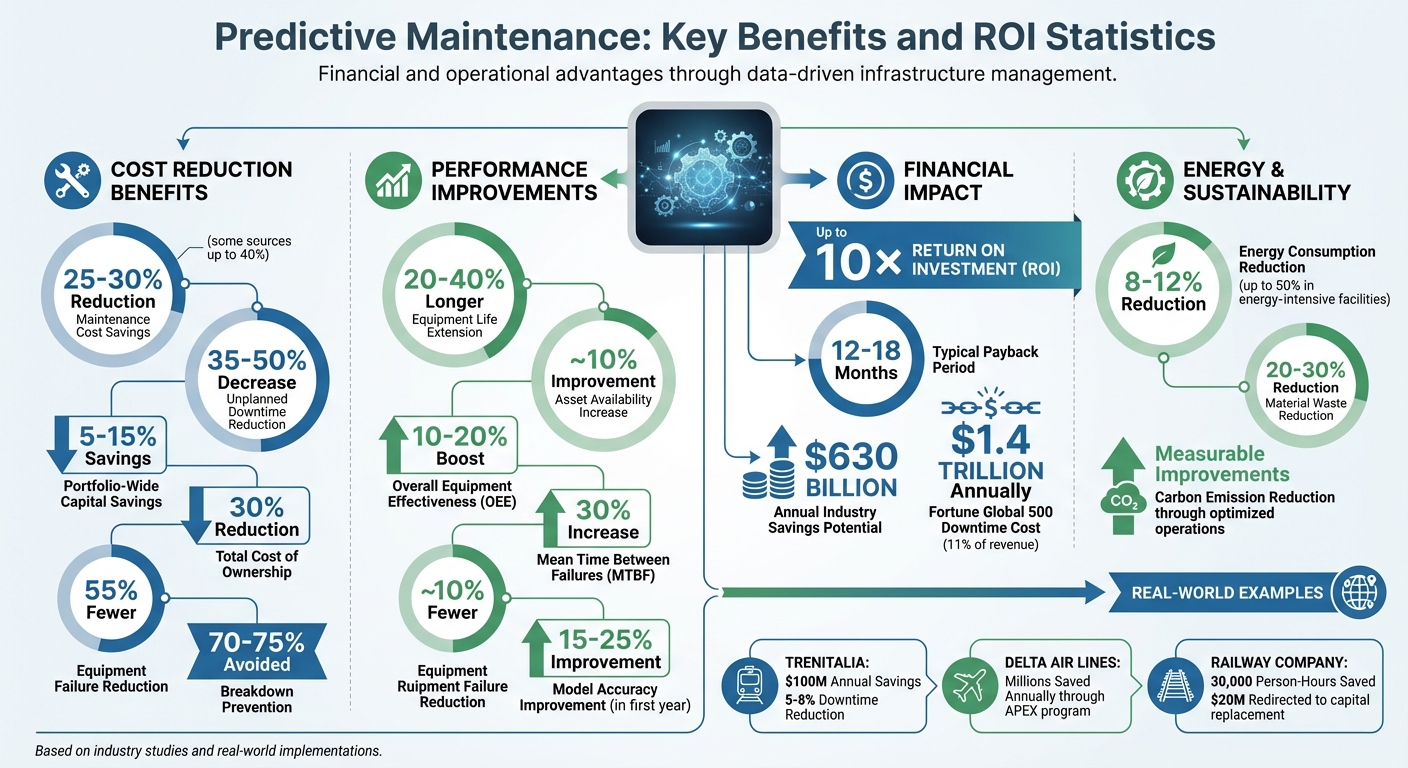
- Predictive Maintenance Saves Money: It reduces unplanned downtime by up to 50% and maintenance costs by 25%-30%.
- Data-Driven Decisions Improve Investments: Real-time data and predictive models enable smarter capital allocation, saving 5%-15% across portfolios.
- Case Studies Prove Results: Examples like Delta Air Lines en Trenitalia show millions saved annually through predictive systems.
This article explains the steps to build a strong data system, including integrating data, using AI for predictions, and aligning maintenance with investment goals. These strategies aren’t just cost-effective – they also improve asset performance and reliability.
Predictive Maintenance ROI: Cost Savings and Performance Improvements
Building Data Infrastructure for Predictive Operations
Core Elements of a Predictive Maintenance Data Foundation
Creating an effective predictive maintenance system hinges on three essential layers: a consolidated historical asset baseline, real-time operational data integration, and universal data standards. Without these working together, even the most advanced analytics tools may fail to provide accurate insights. Skipping these foundational steps often results in costly systems that can’t answer fundamental questions about when to repair or replace critical assets.
Building an Asset Baseline from Historical Data
Every predictive model needs a clear starting point: a detailed picture of what assets you own, where they are, and how they’ve performed over time. This requires consolidating records like asset inventories, historical performance data, maintenance logs, and external factors like environmental conditions [1][2]. The accuracy of predictions relies heavily on having a comprehensive record of past maintenance activities, recurring expenditures, work orders, labor needs, and warranty details [2][1]. Key data points should also include asset age, current value, and specific component details [2].
For assets exposed to external conditions, additional data like historical weather patterns, seismic activity, and criticality assessments can help identify external stressors that accelerate wear and tear [1]. Establishing this baseline is an investment – assessments for a 500,000-square-foot facility typically range from $35,000 to $300,000 [2].
The National Research Council emphasizes the importance of a "knowledge-based" approach, where decisions about inspections and schedules are driven by quantifiable information rather than arbitrary timelines [2]. Additionally, the "no data before their time" principle ensures that data collection focuses only on information directly tied to decision-making, avoiding unnecessary costs [2].
Once this historical foundation is in place, the next step involves integrating real-time operational data to predict future performance.
Real-Time Data Collection and Integration
While historical data provides a look into the past, real-time data reveals where things are headed. Modern predictive maintenance systems rely on continuous streams of operational telemetry – such as vibration, temperature, fluid levels, and energy use – to define normal behavior and train anomaly detection models [6]. The real challenge lies not in collecting this data but in integrating it across various systems without creating new silos.
Hybrid architectures offer an effective solution. By combining edge computing gateways for immediate anomaly detection with cloud platforms for deeper analysis, organizations can process data locally while still leveraging machine learning for long-term insights [7][8]. This approach works across equipment from multiple manufacturers without requiring hardware replacements [7]. With IoT sensors priced between $0.10 and $0.80 per unit, broad instrumentation of assets is now more feasible than ever [7].
API-driven integration ensures predictive insights flow seamlessly into existing systems like Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) [7][8]. For instance, when an anomaly is detected, it can automatically trigger a work order in the organization’s current maintenance system. Different environments may require diverse connectivity solutions, including both wired protocols like Modbus and wireless options like LoRaWAN or WiFi [7].
Companies like Delta Air Lines illustrate the value of this integration. Their APEX program, powered by AI-driven predictive maintenance, saved them millions annually and earned the 2024 Aviation Week Innovation Award [7]. Evenzo, EasyJet avoided 35 technical cancellations in a single month by leveraging predictive insights [7].
To ensure success, it’s crucial to maintain high data quality. Starting with pilot projects on critical systems – like baggage handling or HVAC equipment – can demonstrate ROI before scaling [7]. Many organizations see returns within 12 to 18 months of implementation [7][8].
Data Consistency and Standardization
The final layer, standardization, ensures seamless communication across systems. Without consistent protocols, classification standards, and centralized asset registers, scaling predictive maintenance beyond pilot projects becomes nearly impossible. As the National Research Council states, "Every system and data item should be directly related to decision-making at some level" [2].
Standardization begins with uniform data collection across the organization, enabling benchmarking and the development of performance metrics [2]. Open protocols for systems like Building Automation Systems (BAS) allow devices from different vendors to communicate effectively [2]. Using equipment-agnostic platforms also prevents vendor lock-in while ensuring smooth data integration with existing CMMS and ERP systems [7].
Equally important is data cleansing and validation. Automated workflows can filter out noise, address missing values, and validate sensor readings before feeding them into predictive models [8]. Dynamic baselines, which adapt to real-world operating conditions using machine learning, outperform static manufacturer benchmarks [8]. With clean, standardized data, advanced anomaly detection algorithms can achieve 92% to 98% accuracy in identifying potential failures 30 to 90 days in advance [7].
The benefits of getting this right are undeniable. Predictive maintenance can lower maintenance costs by 20% to 30% and extend equipment life by 20% to 40% [8]. AI-driven systems further boost equipment availability by 15% to 25% and reduce unplanned maintenance by 35% to 50% [7]. Achieving these outcomes requires treating data as a critical asset throughout its lifecycle [1].
As noted by the Nationale Academies voor Wetenschappen, Techniek en Geneeskunde:
"Effective transportation asset management (TAM) depends on having good data about the assets under management, their descriptions, current condition and history, functional performance, and the activities conducted to develop, maintain, improve, and rehabilitate them" [5].
Linking Predictive Maintenance Data to Investment Planning
With a solid data foundation in place, the next step is bridging the gap between current operations and future investment needs. Predictive maintenance evolves from simply diagnosing problems to becoming a strategic tool that ties asset health to capital planning. This approach enables investment decisions that are firmly grounded in the condition of assets.
Forecasting Asset Degradation and Lifecycle Costs
Traditional capital planning often relies on manufacturer guidelines and fixed schedules, which don’t always reflect how assets actually age. Predictive models, built on unified data platforms, change this by combining historical maintenance records with real-time sensor data. These models create detailed lifecycle curves, offering a clearer picture of when components are likely to fail [1][13].
By calculating Remaining Useful Life (RUL) with greater precision, organizations can allocate capital at the right time, avoiding premature replacements. This approach also helps identify "budgetary sinkholes" – assets that are over-maintained when replacement would be more cost-effective – ensuring capital is used more efficiently.
The financial impact is striking. Companies that integrate predictive maintenance into capital planning often see portfolio savings of 5% to 15% [1], cut maintenance expenses by 18% to 25% [9], and extend asset life by 20% to 40% [12]. A "Weighted Slope" model has proven highly accurate, predicting asset degradation 92% of the time compared to traditional methods [13].
"Advanced analytics can help owners prioritize replacement or repair of specific components rather than a complete asset." – John Levene, Associate Partner, McKinsey [1]
Risk-Based Prioritization of Maintenance and Investments
Not all assets carry the same level of risk. For example, a failed HVAC unit in a storage room is inconvenient, but a cooling failure in a data center could result in millions of dollars in losses. Risk-based prioritization uses predictive data to rank projects by their criticality, compliance needs, safety concerns, and performance impact. This shifts the focus from routine calendar-based inspections to condition-based assessments tailored to each asset’s service life [2].
As the National Research Council states, "every system and data item should be directly related to decision-making at some level" [2].
Three key elements drive effective prioritization:
- Incorporating predictive insights into capital planning
- Using advanced analytics powered by IoT and machine learning
- Building expertise within the organization to manage these tools [1]
By reallocating resources from low-risk, over-maintained assets to high-risk areas, companies can prevent costly failures. The stakes are substantial – unplanned downtime costs Fortune Global 500 companies about 11% of their revenue annually, translating to $1.4 trillion [10][11]. Predictive maintenance, with its early warning systems, helps mitigate these disruptions.
Connecting Maintenance and Investment Goals with Energy and Carbon Targets
Predictive data doesn’t just improve asset performance; it also supports sustainability goals. Equipment in poor condition often consumes more energy. For instance, motors with bearing issues use more current, and compressors with valve problems must work harder to maintain pressure [8]. Addressing these issues early can cut energy consumption by 8% to 12% [8].
Unlike traditional maintenance approaches that often replace components prematurely – leaving 40% to 60% of their useful life unused – predictive maintenance ensures parts are replaced only when necessary. This reduces material waste by 20% to 30% [8]. The environmental benefits extend to less frequent large-scale replacements, which typically involve carbon-intensive activities like new construction and material production [8][13].
Real-time data from Building Automation Systems further helps managers find the optimal balance between production and energy efficiency [8][2]. Companies using advanced analytics for capital planning have been able to redirect 5% to 15% of their portfolio savings toward sustainability-focused upgrades [1]. This creates a win-win scenario: lower operational costs and measurable progress toward ESG and regulatory compliance goals.
sbb-itb-5be7949
Technology and Tools for Predictive Insights
Today’s technology leverages AI, simulation, and real-time dashboards to transform raw asset data into practical insights for maintenance and investment decisions. This tech ecosystem builds on existing data frameworks, connecting day-to-day operations with long-term strategic planning.
AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning plays a central role in predictive maintenance. It uses historical data for supervised learning, anomaly detection through unsupervised methods, and reinforcement learning to refine maintenance schedules over time [17][18].
The financial benefits are hard to ignore. AI-driven predictive maintenance can slash equipment downtime by up to 50%, extend the life of assets by 20% to 40%, and cut maintenance costs by as much as 40% [15]. Companies adopting this approach typically see a 25% to 30% drop in maintenance expenses compared to reactive models, while avoiding 70% to 75% of unplanned breakdowns [17][18][19].
Real-world examples back up these numbers. Between 2014 and 2017, Trenitalia, Italy’s train operator, invested $500 million to equip 1,500 locomotives with sensors. Data streamed to a private cloud for analysis helped reduce downtime by 5% to 8% and cut annual maintenance costs by 8% to 10%, saving $100 million annually [20]. Evenzo, GE Aviation uses sensors in its 44,000 jet engines to send data to monitoring centers in Cincinnati and Shanghai. By combining sensor readings with engine models, the system predicts maintenance needs before failures occur, lowering costs and improving safety [16].
"AI-driven predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by up to 50% and extend equipment life by 20 to 40%, which ultimately can generate savings of up to $630 billion annually across various industries." – Subanu Senthilkumar, AI Advocate [15]
Emerging technologies are adding new layers of capability. Computer vision detects subtle wear and tear, while generative AI allows technicians to interact with maintenance logs in natural language and automatically create work orders [16][18]. By 2028, one-third of enterprise applications are expected to feature AI systems capable of semi-autonomous decision-making [18].
Digital Twins and Scenario Modeling
Digital twins take AI insights further by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, offering a risk-free way to test investment strategies. By integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) with dynamic simulation, these tools combine static data with real-time performance metrics, enabling smarter long-term planning [21][1].
This shift enables organizations to move from time-based maintenance schedules to condition-based decisions, avoiding premature replacements and reallocating funds to higher-impact projects [1].
Bijvoorbeeld, Melbourne Water adopted IBM Maximo to analyze energy data across its facilities. The system uses AI to optimize energy consumption, improving efficiency and cutting carbon emissions through smarter maintenance and operations [18]. At Aalborg University, a digital twin project combining BIM with predictive control reduced heating demand by 15% [21].
"Digital twins… provide a risk-free digital laboratory for testing designs and options, improving efficiency and time to market, for example, by optimizing scheduling, sequencing, and maintenance." – McKinsey & Company [22]
Currently, 75% of large enterprises are investing in digital twins to scale their AI capabilities [22]. These tools are increasingly paired with generative AI to automate simulation code creation and offer natural language interfaces for complex decision-making [22].
Automated Dashboards and Decision Support Systems
Real-time dashboards and automated systems are streamlining predictive analytics. These dashboards consolidate data from sources like IoT sensors, Building Automation Systems, and business applications into a unified view, enabling faster and better-informed decisions [23][8]. AI enhances these systems by prioritizing maintenance tasks based on severity and risk, ensuring teams focus on critical issues [14][8].
The most effective dashboards provide context-rich alerts, detailing the affected asset, potential failure mode, recommended actions, required parts, and estimated labor hours [8]. Alerts are delivered through dashboards, emails, or SMS, helping organizations achieve a 40% to 50% reduction in unplanned downtime [8].
Automation is a game-changer here. By integrating with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), these platforms can automatically generate work orders from predictive insights. This minimizes the delay between detection and resolution, avoiding the steep costs associated with emergency repairs, such as overtime and expedited shipping [23][8].
Strategic tools also help align asset health with broader organizational objectives. Metrics like the Mission Dependency Index (MDI) of Prioriteit Activa Index (API) connect asset performance to mission goals and stakeholder needs [3]. "What-if" simulations allow managers to explore different investment scenarios and prioritize based on budget constraints [1][2].
"The AI solution could serve as an omnipresent maintenance employee helping the human workforce make better decisions about when and where to target operations." – Deloitte [14]
Thanks to affordable IoT sensors and cloud computing, these advanced decision-support systems are now accessible to a wider range of organizations, not just high-budget industries like aerospace [8]. The transition from static, time-based benchmarks to dynamic, real-time data is paving the way for more precise and cost-efficient maintenance strategies [1][2].
Implementation Steps and Measuring Results
Phased Approach to Data Collection and Integration
Begin by conducting a criticality assessment to pinpoint the assets that contribute most to production losses, high repair expenses, or safety concerns. It’s often just a small group of assets that accounts for the majority of these issues [24].
Start with a pilot program targeting a specific asset group before rolling out changes across the organization. For example, in 2024, E. & J. Gallo Winery applied this phased approach as part of its "World Class Maintenance" initiative. They focused on their crushing area, particularly stemming machines that were traditionally overhauled annually regardless of their condition. By installing wireless vibration monitors and edge analytics devices, they detected a lubrication issue on a critical turret bearing early. This allowed them to schedule a repair instead of facing an emergency shutdown [27].
Assemble a cross-functional team led by a strategic asset maintenance expert and follow a three-step process: Design and Data Ingestion (gathering internal and external records), Proof of Concept (testing models against past events to validate the approach), and Integrate and Scale (deploying real-time predictive capabilities) [1][25].
Keep in mind that data preparation can take up to 80% of the project’s timeline. Raw sensor data often includes noise, duplicates, and gaps, which need to be addressed. Standardizing sensor formats and timestamps upfront is crucial to avoid model corruption. Also, balance monitoring frequencies – track critical equipment continuously while less critical assets can report data hourly or daily [24].
"The efforts spent building a predictive maintenance environment today will pay dividends in competitive advantage in the coming decades."
– Tom Francisco, Reliability Subject Matter Expert, Emerson [27]
These structured steps lay the foundation for effective performance measurement through well-defined KPIs.
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Once the system is operational, measuring its impact becomes vital.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), balancing operational expenses (OPEX) against capital expenditures (CAPEX). Organizations typically report a 30% reduction in ownership costs, 55% fewer unplanned equipment failures, and a 30% increase in Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) [26][28][24].
Track asset availability, which often improves by approximately 10%, while also reducing reactive maintenance needs and extending asset lifespans. For example, one railway company saved over 30,000 person-hours annually and redirected $20 million in engine-overhaul costs toward capital replacement [26][1].
Monitor model accuracy as it evolves. Expect prediction accuracy to improve by 15% to 25% in the first year through feedback loops. Additionally, organizations typically experience a 10% to 20% boost in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) [24][26].
Include sustainability metrics in your analysis, such as reductions in carbon emissions and improvements in energy efficiency. Most organizations see measurable gains in reliability and cost savings within 6 to 12 months of implementation [28].
Case Studies and Applications
Case studies consistently show that predictive maintenance can drastically reduce operating costs and save significant labor hours [1][27]. Industry examples further illustrate how successful pilot programs deliver quick ROI [27].
These real-world examples highlight how strong data management practices can drive tangible operational improvements. By starting small, proving value early, and scaling systematically, organizations can cut operating costs by as much as 50% while enhancing service quality across their portfolios.
Conclusion: Building a Data-Driven Approach to Maintenance and Investment Planning
A strong data foundation can completely reshape how infrastructure is managed. Moving from reactive fixes to decisions based on asset conditions can yield impressive results. For example, this shift has been shown to reduce maintenance costs by 30–40% and cut equipment downtime by 35–45% [29]. On a broader scale, advanced analytics can lead to portfolio-wide savings of 5–15% by enabling smarter capital planning [1].
To get started, focus on three key areas [1]: incorporating predictive insights into your capital planning, linking real-time data with long-term forecasts, and building the necessary expertise to support these changes. As ISO 55000 puts it, "Asset management is not about the asset, but about the value generated by the asset" [30]. A well-structured data strategy ensures every dollar invested delivers maximum value. These principles provide a clear roadmap for taking actionable first steps.
Start by prioritizing your most critical assets. Launch a focused pilot project to demonstrate the benefits, then expand gradually. Ensure data consistency by standardizing how assets are identified. Use tools like the Mission Dependency Index (MDI) or Asset Priority Index (API) to tie maintenance decisions directly to your organization’s strategic goals [30].
The financial advantages of these strategies are undeniable. Predictive maintenance alone can deliver up to 10× ROI, reduce costs by 25–30%, and prevent 70–75% of breakdowns [29]. In energy-intensive facilities, data-driven upgrades can also slash energy use by as much as 50% [4]. These savings not only free up funds for other priorities but also extend the lifespan of assets and improve overall service quality.
Organizations that invest in building strong data foundations today will be better equipped to tackle future challenges – whether it’s meeting compliance requirements, achieving sustainability goals, or managing tight budgets. By taking action now, you can unlock these benefits across your entire portfolio and set your organization up for long-term success.
FAQs
How does predictive maintenance help lower costs and improve equipment reliability?
Predictive maintenance is all about cutting costs and boosting equipment reliability by leveraging advanced analytics en real-time data to predict potential failures. Instead of waiting for something to break down or sticking to a rigid maintenance schedule, this method allows for maintenance to be done only when it’s truly needed. The result? You avoid costly unplanned downtime and skip unnecessary repairs.
This approach also keeps equipment running in top condition, which reduces the chances of sudden breakdowns and helps extend the life of your assets. Over time, this means more consistent performance, smarter use of resources, and lower overall maintenance expenses – all contributing to smoother, more efficient operations.
What are the essential steps to create a strong data foundation for predictive maintenance?
To set up a reliable foundation for predictive maintenance, start by gathering precise and detailed data from all your assets. This includes everything from sensor readings to maintenance records and operational performance metrics. The key here is quality – accurate data leads to better predictions and smarter decisions.
Next, move this data into a centralized, scalable system. If you’re still relying on scattered spreadsheets, it’s time to upgrade. A dedicated platform ensures your data stays consistent and can handle the demands of larger operations. With this setup in place, you can leverage advanced analytics, such as machine learning, to anticipate maintenance needs, improve performance, and minimize the risk of unexpected equipment failures.
Lastly, implement strong data governance practices. This step is crucial to maintaining data quality and staying compliant with regulatory and audit standards. By focusing on these core areas – data collection, centralized systems, analytics, and governance – you’ll create a reliable framework for predictive maintenance that supports smarter decision-making and long-term planning.
How does integrating real-time data improve investment planning?
Integrating real-time data into investment planning provides organizations with accurate and up-to-date insights into how assets are performing and their current operational conditions. This means companies can quickly spot problems, address inefficiencies, and make informed decisions to avoid expensive breakdowns. It also allows for better-timed maintenance schedules, cutting down on downtime and helping assets last longer.
In addition, real-time data enhances forecasting and risk assessment. Planners can evaluate different investment strategies based on current conditions, aligning spending with actual asset needs and performance trends. This approach helps create infrastructure plans that are not only cost-effective but also more adaptable and efficient. By relying on the latest data, decisions are rooted in present realities rather than outdated information.
Verwante Blog Berichten
- Voorspellend onderhoud voor activabeheer (infrastructuur en onroerend goed) is van cruciaal belang – raadpleeg de website: https://theiam.org
- Hoe voorspellend onderhoud (zonder IoT en realtime) waarde toevoegt voor eigenaren van infrastructuur en gebouwen
- Voorspellend onderhoud en ROI
- Verouderde infrastructuur en levenscyclusbeheer
